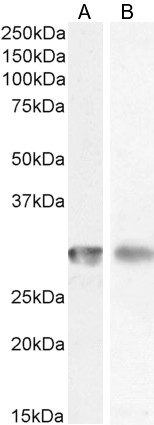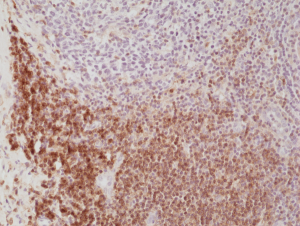
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human Tonsil tissue section using anti-CD4 rabbit monoclonal antibody (CloneRM345) at a 1:500 dilution.
anti-CD4 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM345)
REV-31-1231-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCD4
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD4 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM345)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM345
- Gene ID920
- Target nameCD4
- Target descriptionCD4 molecule
- Target synonymsCD4mut, IMD79, Leu-3, OKT4D, T4, T-cell surface glycoprotein CD4, CD4 antigen (p55), CD4 receptor, T-cell surface antigen T4/Leu-3
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP01730
- Protein NameT-cell surface glycoprotein CD4
- Scientific DescriptionHuman CD4 is a cell surface glycoprotein of 55kDa expressed on most thymocytes, on about two thirds of peripheral T helper cells and on some monocyte macrophage lineage cells and dendritic cells. CD4 interacts with MHC Class II molecules in an accessory role during foreign antigen recognition by T cells. The extracellular portion of CD4 is an array of four Ig-like domains. The N-terminal region of CD4 is a receptor for the HIV-1 viral protein gp120. At the tissue level, CD4 expression may be detected in thymus, lymph nodes, tonsils, and spleen and also in specific regions of the brain, gut and other non-lymphoid tissues. CD4 functions to initiate or augment the early phase of T cell activation through its association with the T cell receptor complex and protein tyrosine kinase, Lck. It may also function as an important mediator of direct neuronal damage in infectious and immune-mediated diseases of the central nervous system. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to the extracellular domain of human CD4. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Human CD4 is a cell surface glycoprotein of 55kDa expressed on most thymocytes, on about two thirds of peripheral T helper cells and on some monocyte macrophage lineage cells and dendritic cells. CD4 interacts with MHC Class II molecules in an accessory role during foreign antigen recognition by T cells. The extracellular portion of CD4 is an array of four Ig-like domains. The N-terminal region of CD4 is a receptor for the HIV-1 viral protein gp120. At the tissue level, CD4 expression may be detected in thymus, lymph nodes, tonsils, and spleen and also in specific regions of the brain, gut and other non-lymphoid tissues. CD4 functions to initiate or augment the early phase of T cell activation through its association with the T cell receptor complex and protein tyrosine kinase, Lck. It may also function as an important mediator of direct neuronal damage in infectious and immune-mediated diseases of the central nervous system.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161