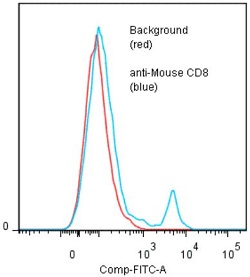
Binding of anti-mCD8alpha (53-6.72) +GAR/FITC to balb-c splenocytes. Method: Tested for binding to ACK lysed murine splenocytes in FACS. Five x 10^5 splenocytes per tube were washed and pre-incubated with 20ul of 300ug/ml murine IgG (to reduce non-specific binding) after which they were incubated 45 minutes on ice with 80ul of anti-CD8 antibody diluted to 10ug/ml. Cells were washed twice and incubated with 2nd reagent Goat anti-Rat IgG/FITC, after which they were washed three times, fixed and analyzed by FACS. An 8.8 % sub population of the cells stained positive with a mean shift of 1.6 log10 fluorescent units when compared to background.
anti-CD8-alpha (mouse), mAb (53-6) (preservative free)
ANC-260-820
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityMouse
TargetCd8a
Overview
- SupplierAncell Corporation
- Product Nameanti-CD8-alpha (mouse), mAb (53-6) (preservative free)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID53-6
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID12525
- Target nameCd8a
- Target descriptionCD8 subunit alpha
- Target synonymsLy-2, Ly-35, Ly-B, Lyt-2, T-cell surface glycoprotein CD8 alpha chain, CD8 antigen, alpha chain, Lyt-2.1 lymphocyte differentiation antigen (AA at 100), T-cell surface glycoprotein Lyt-2
- HostRat
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Protein IDP01731
- Protein NameT-cell surface glycoprotein CD8 alpha chain
- Scientific DescriptionCD8 identifies cytotoxic/suppressor T cells that interact with MHC Class I bearing targets. CD8 is thought to play a role in the process of T cell mediated killing. CD8-alpha chains binds to Class I MHC molecules alpha-3 domains. Defects in CD8A are a cause of familial CD8 deficiency. Familial CD8 deficiency is a novel autosomal recessive immunologic defect characterized by absence of CD8+ cells, leading to recurrent bacterial infections. - Monoclonal Antibody. Isotype: Rat IgG2akappa. Immunogen: Murine thymocytes/splenocytes. Applications: ELISA, FACS. 50 mM Sodium Phosphate pH 7.5, 100mM KCl, 150mM NaCl. CD8 identifies cytotoxic/suppressor T cells that interact with MHC Class I bearing targets. CD8 is thought to play a role in the process of T cell mediated killing. CD8-alpha chains binds to Class I MHC molecules alpha-3 domains. Defects in CD8A are a cause of familial CD8 deficiency. Familial CD8 deficiency is a novel autosomal recessive immunologic defect characterized by absence of CD8+ cells, leading to recurrent bacterial infections.
- ReactivityMouse
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161




