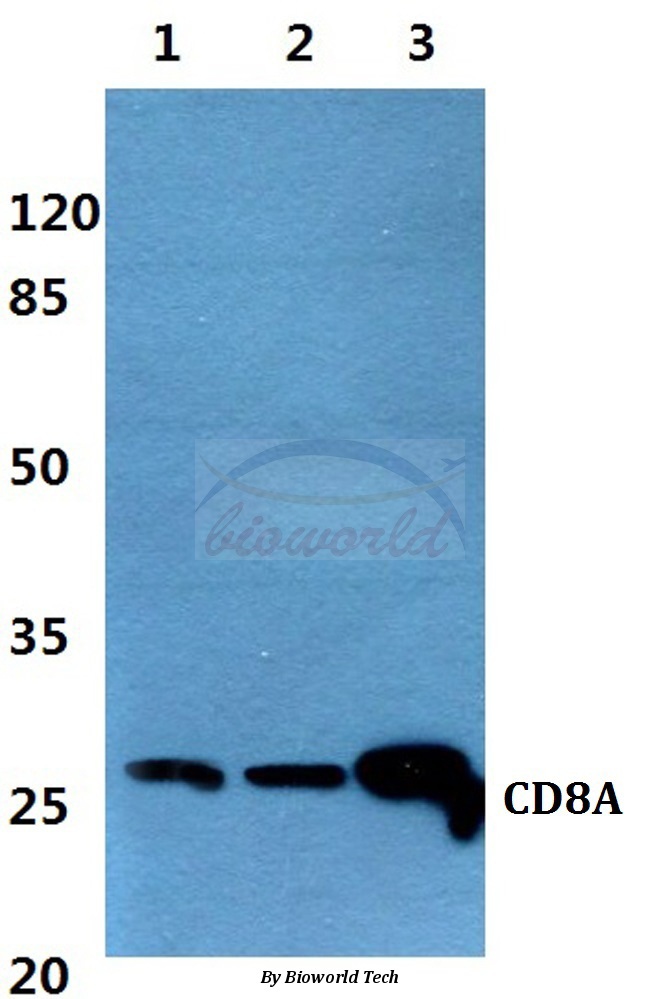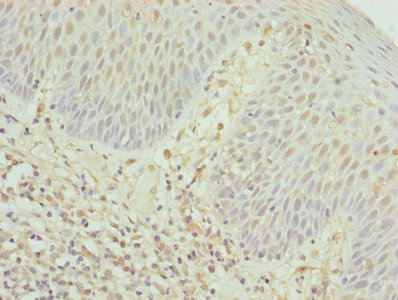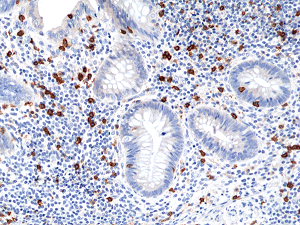
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human appendix tissue section using anti-CD8a rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM397) at a 1:100 dilution.
anti-CD8a (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM397)
REV-31-1283-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCD8A
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-CD8a (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM397)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM397
- Gene ID925
- Target nameCD8A
- Target descriptionCD8 subunit alpha
- Target synonymsCD8, CD8alpha, IMD116, Leu2, p32, T-cell surface glycoprotein CD8 alpha chain, CD8 antigen, alpha polypeptide (p32), CD8a molecule, Leu2 T-lymphocyte antigen, OKT8 T-cell antigen, T cell co-receptor, T-cell antigen Leu2, T-lymphocyte differentiation antigen T8/Leu-2, T8 T-cell antigen
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP01732
- Protein NameT-cell surface glycoprotein CD8 alpha chain
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human CD8a. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. The CD8 antigen is a cell surface glycoprotein found on most cytotoxic T lymphocytes that mediates efficient cell-cell interactions within the immune system. The CD8 antigen, acting as a coreceptor, and the T-cell receptor on the T lymphocyte recognize antigens displayed by an antigen-presenting cell (APC) in the context of class I MHC molecules. The functional coreceptor is either a homodimer composed of two alpha chains, or a heterodimer composed of one alpha and one beta chain. Both alpha and beta chains share significant homology to immunoglobulin variable light chains. CD8 positive immunostaining results may aid in identifying T-cell lymphomas and in identifying the T cytotoxic/suppressor cell subset of T lymphocytes in normal tissues. Defects in CD8A are a cause of familial CD8 deficiency (CD8 deficiency). Familial CD8 deficiency is a novel autosomal recessive immunologic defect characterized by absence of CD8+ cells, leading to recurrent bacterial infections. - The CD8 antigen is a cell surface glycoprotein found on most cytotoxic T lymphocytes that mediates efficient cell-cell interactions within the immune system. The CD8 antigen, acting as a coreceptor, and the T-cell receptor on the T lymphocyte recognize antigens displayed by an antigen-presenting cell (APC) in the context of class I MHC molecules. The functional coreceptor is either a homodimer composed of two alpha chains, or a heterodimer composed of one alpha and one beta chain. Both alpha and beta chains share significant homology to immunoglobulin variable light chains. CD8 positive immunostaining results may aid in identifying T-cell lymphomas and in identifying the T cytotoxic/suppressor cell subset of T lymphocytes in normal tissues. Defects in CD8A are a cause of familial CD8 deficiency (CD8 deficiency). Familial CD8 deficiency is a novel autosomal recessive immunologic defect characterized by absence of CD8+ cells, leading to recurrent bacterial infections.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161