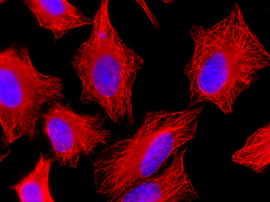
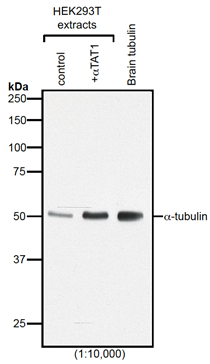
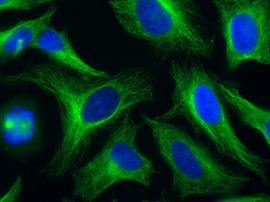
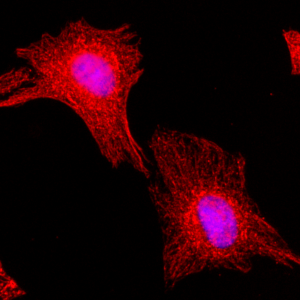
anti-Delta2-Tubulin, pAb (IN120)
AG-25B-0044
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityAll Species, Human, Mouse, Rat
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-Delta2-Tubulin, pAb (IN120)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.5 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- HostRabbit
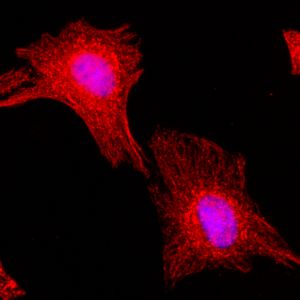
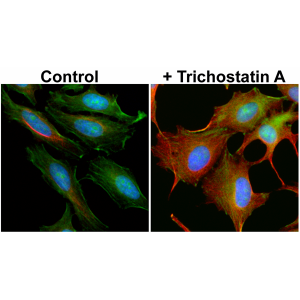
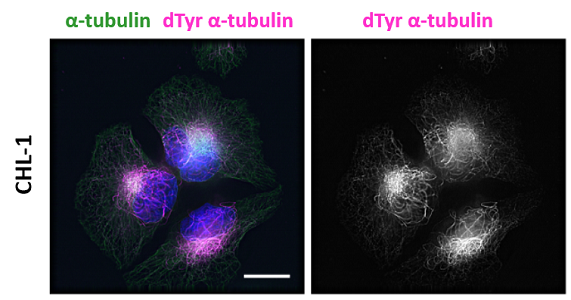
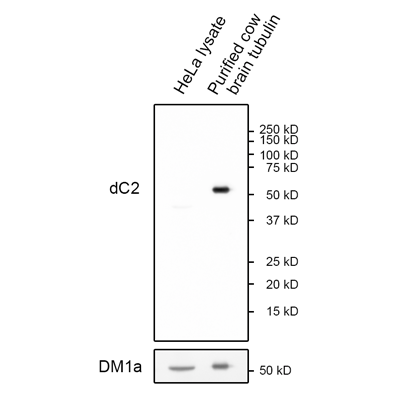
- Scientific DescriptionMicrotubules are key elements of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton that dynamically assemble from heterodimers of alpha- and beta-tubulin. Two different mechanisms can generate microtubule diversity: the expression of different alpha- and beta-tubulin genes, referred to as tubulin isotypes, and the generation of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) on alpha- and beta-tubulin. Tubulin PTMs include the well-known acetylation or phosphorylation, and others that have so far mostly been found on tubulin, detyrosination/tyrosination, polyglutamylation and polyglycylation. These PTMs might have evolved to specifically regulate tubulin and microtubule functions. Delta 2 tubulin (delta2-tubulin) is a specific posttranslationally modified form of alpha-tubulin. It is characterized by the removal of the C-terminal tyrosine residue (detyrosination) and an additional cleavage of the next-to-last glutamic acid residue, resulting in a truncated C-terminal tail. This modification makes delta2-tubulin distinct from other tubulin isoforms and modifications. delta2-tubulin is primarily found in stable microtubules, such as those in neurons, centrioles, and cilia. It is abundant in tissues with long-lived, highly specialized structures. The removal of the C-terminal residues is associated with increased microtubule stability, making delta2-tubulin a marker for stable, long-lived microtubule networks and plays a critical role in cellular processes requiring stable microtubules, such as intracellular trafficking, cell shape maintenance, and the proper functioning of axons and dendrites in neurons. delta2-tubulin is also enriched in the microtubules of axonemes (the structural core of cilia and flagella), where it contributes to the structural integrity and function of these organelles. delta2-tubulin supports the stability of microtubules in neurons, aiding in the maintenance of axonal transport and synaptic connections. It is involved in centrosome organization and mitotic spindle stability, contributing to accurate cell division and it plays a role in maintaining the structural and functional integrity of motile cilia and flagella. Abnormalities in delta2-tubulin levels or distribution have been associated with various conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases, ciliary dysfunction disorders or cancer. - Polyclonal Antibody. This antibody recognises the posttranslationally modified form of alpha-tubulin known as delta2-tubulin. This modification is generated after enzymatic removal of two C-terminal amino acids, Y and E in a process of detyrosination (removal of Y by detyrosinating enzymes from the VASH and the MATCAP/TMCP families), followed by the removal of the penultimate E residue by enzymes from the cytosolic carboxy peptidase (CCP) family. Application: IF, ICC, WB. Source: Rabbit. Microtubules are key elements of the eukaryotic cytoskeleton that dynamically assemble from heterodimers of alpha- and beta-tubulin. Two different mechanisms can generate microtubule diversity: the expression of different alpha- and beta-tubulin genes, referred to as tubulin isotypes, and the generation of posttranslational modifications (PTMs) on alpha- and beta-tubulin. Tubulin PTMs include the well-known acetylation or phosphorylation, and others that have so far mostly been found on tubulin, detyrosination/tyrosination, polyglutamylation and polyglycylation. These PTMs might have evolved to specifically regulate tubulin and microtubule functions. Delta 2 tubulin (delta2-tubulin) is a specific posttranslationally modified form of alpha-tubulin. It is characterized by the removal of the C-terminal tyrosine residue (detyrosination) and an additional cleavage of the next-to-last glutamic acid residue, resulting in a truncated C-terminal tail. This modification makes delta2-tubulin distinct from other tubulin isoforms and modifications. delta2-tubulin is primarily found in stable microtubules, such as those in neurons, centrioles, and cilia. It is abundant in tissues with long-lived, highly specialized structures. The removal of the C-terminal residues is associated with increased microtubule stability, making delta2-tubulin a marker for stable, long-lived microtubule networks and plays a critical role in cellular processes requiring stable microtubules, such as intracellular trafficking, cell shape maintenance, and the proper functioning of axons and dendrites in neurons. delta2-tubulin is also enriched in the microtubules of axonemes (the structural core of cilia and flagella), where it contributes to the structural integrity and function of these organelles. delta2-tubulin supports the stability of microtubules in neurons, aiding in the maintenance of axonal transport and synaptic connections. It is involved in centrosome organization and mitotic spindle stability, contributing to accurate cell division and it plays a role in maintaining the structural and functional integrity of motile cilia and flagella. Abnormalities in delta2-tubulin levels or distribution have been associated with various conditions, including neurodegenerative diseases, ciliary dysfunction disorders or cancer.
- ReactivityAll Species, Human, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161