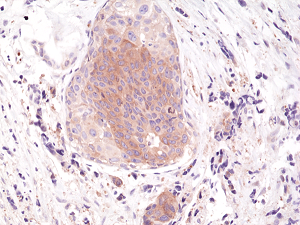
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human breast cancer tissue section using anti-phospho-eIF-2alpha (Ser51) rabbit monoclonal antibody (clone RM298) at a 1:200 dilution.
anti-eIF-2 alpha (pS51) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM298)
REV-31-1183-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetEIF2S1
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-eIF-2 alpha (pS51) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM298)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM298
- Gene ID1965
- Target nameEIF2S1
- Target descriptioneukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit alpha
- Target synonymsEIF-2, EIF-2A, EIF-2alpha, EIF2, EIF2A, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 1, eIF-2-alpha, eIF2-alpha, eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2, subunit 1 alpha, 35kDa
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP05198
- Protein NameEukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit 1
- Scientific DescriptionEukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 (eIF2) is a eukaryotic initiation factor. It is required for most forms of eukaryotic translation initiation. eIF2 mediates the binding of tRNAiMet to the ribosome in a GTP-dependent manner. eIF2 is a heterotrimer consisting of an alpha (also called subunit 1, EIF2S1), a beta (subunit 2, EIF2S2), and a gamma (subunit 3, EIF2S3) subunit. eIF2 activity is regulated by a mechanism involving both guanine nucleotide exchange and phosphorylation. Phosphorylation takes place at the alpha-subunit, which is a target for a number of serine kinases that phosphorylate serine 51. Those kinases act as a result of stress such as amino acid deprivation (GCN2), ER stress (PERK), the presence of dsRNA (PKR) heme deficiency (HRI), or interferon. Once phosphorylated, eIF2 shows increased affinity for its Guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B. Increased concentrations of inactive (phosphorylated) eIF2 were found in patients suffering from neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimers, Parkinsons, and Huntingtons disease. EIF2a (Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2A) is a heterotrimer composed of three subunits (alpha, beta and gamma). This translation initiation factor drives binding of initiator methionyl-tRNA to the 40S ribosome to form the 43S pre-initiation complex. The polypeptide can be phosphorylated by related protein kinases activated in response to stress. Phosphorylated eIF2alpha prevents the recycling of the eIF2-bound GDP to GTP by the guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) eIF2B. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human eIF-2a (eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2 subunit alpha) only when phosphorylated at Ser51. There is no cross-reactivity to eIF-2a without phosphorylation at Ser51. This antibody may also react to mouse or rat Phospho-eIF-2a (Ser51). Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Eukaryotic Initiation Factor 2 (eIF2) is a eukaryotic initiation factor. It is required for most forms of eukaryotic translation initiation. eIF2 mediates the binding of tRNAiMet to the ribosome in a GTP-dependent manner. eIF2 is a heterotrimer consisting of an alpha (also called subunit 1, EIF2S1), a beta (subunit 2, EIF2S2), and a gamma (subunit 3, EIF2S3) subunit. eIF2 activity is regulated by a mechanism involving both guanine nucleotide exchange and phosphorylation. Phosphorylation takes place at the alpha-subunit, which is a target for a number of serine kinases that phosphorylate serine 51. Those kinases act as a result of stress such as amino acid deprivation (GCN2), ER stress (PERK), the presence of dsRNA (PKR) heme deficiency (HRI), or interferon. Once phosphorylated, eIF2 shows increased affinity for its Guanine nucleotide exchange factor eIF2B. Increased concentrations of inactive (phosphorylated) eIF2 were found in patients suffering from neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimers, Parkinsons, and Huntingtons disease. EIF2a (Eukaryotic translation initiation factor 2A) is a heterotrimer composed of three subunits (alpha, beta and gamma). This translation initiation factor drives binding of initiator methionyl-tRNA to the 40S ribosome to form the 43S pre-initiation complex. The polypeptide can be phosphorylated by related protein kinases activated in response to stress. Phosphorylated eIF2alpha prevents the recycling of the eIF2-bound GDP to GTP by the guanine nucleotide exchange factor (GEF) eIF2B.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161


![eIF2 alpha antibody [N1C3] detects eIF2 alpha protein at cytoplasm by immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HCT 116 cells were fixed in 4% paraformaldehyde at RT for 15 min. Green: eIF2 alpha protein stained by eIF2 alpha antibody [N1C3] (GTX101241) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33342 staining.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX101241/GTX101241_42774_20170628_IFA_w_23060100_284.webp)

