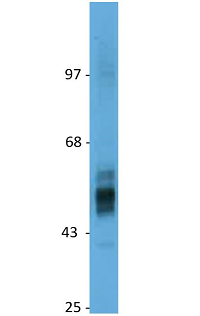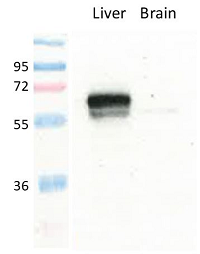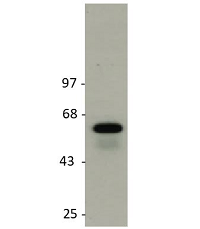
Figure 1: Detection of endogenous rat GLUT2 in rat liver membranes by immunoblotting using anti-GLUT2 (rat), pAb (IN119) (Prod. No. AG-25B-0043).
anti-GLUT2 (rat), pAb (IN119)
AG-25B-0043
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityRat
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-GLUT2 (rat), pAb (IN119)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- HostRabbit
- Protein IDP12336
- Protein NameSolute carrier family 2, facilitated glucose transporter member 2
- Scientific DescriptionGLUT2 belongs to the family of glucose transporters (GLUTs, encoded by the SLC2A genes), which comprises 14 isoforms. GLUT2 has a uniquely low affinity for glucose (Km ~ 17mmol/l), and can also use mannose, galactose and fructose as low-affinity substrates. However, it has a high affinity for glucosamine (Km ~ 0.8mmol/l). GLUT2 is expressed in liver, intestine, kidney and pancreatic islet beta cells, as well as in the central nervous system, in neurons, astrocytes and tanycytes. Physiological studies of genetically modified mice have revealed a role for GLUT2 in several regulatory mechanisms. GLUT2 is also the major glucose transporter in the plasma membrane of hepatocytes. In pancreatic beta cells, GLUT2 is required for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. In the nervous system, GLUT2-dependent glucose-sensing controls feeding, thermoregulation and pancreatic islet cell mass and function, as well as sympathetic and parasympathetic activities. - Polyclonal Antibody. Recognizes rat GLUT2. Applications: IHC, IP, WB. Source: Rabbit. GLUT2 belongs to the family of glucose transporters (GLUTs, encoded by the SLC2A genes), which comprises 14 isoforms. GLUT2 has a uniquely low affinity for glucose (Km ~ 17mmol/l), and can also use mannose, galactose and fructose as low-affinity substrates. However, it has a high affinity for glucosamine (Km ~ 0.8mmol/l). GLUT2 is expressed in liver, intestine, kidney and pancreatic islet beta cells, as well as in the central nervous system, in neurons, astrocytes and tanycytes. Physiological studies of genetically modified mice have revealed a role for GLUT2 in several regulatory mechanisms. GLUT2 is also the major glucose transporter in the plasma membrane of hepatocytes. In pancreatic beta cells, GLUT2 is required for glucose-stimulated insulin secretion. In the nervous system, GLUT2-dependent glucose-sensing controls feeding, thermoregulation and pancreatic islet cell mass and function, as well as sympathetic and parasympathetic activities.
- ReactivityRat
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161