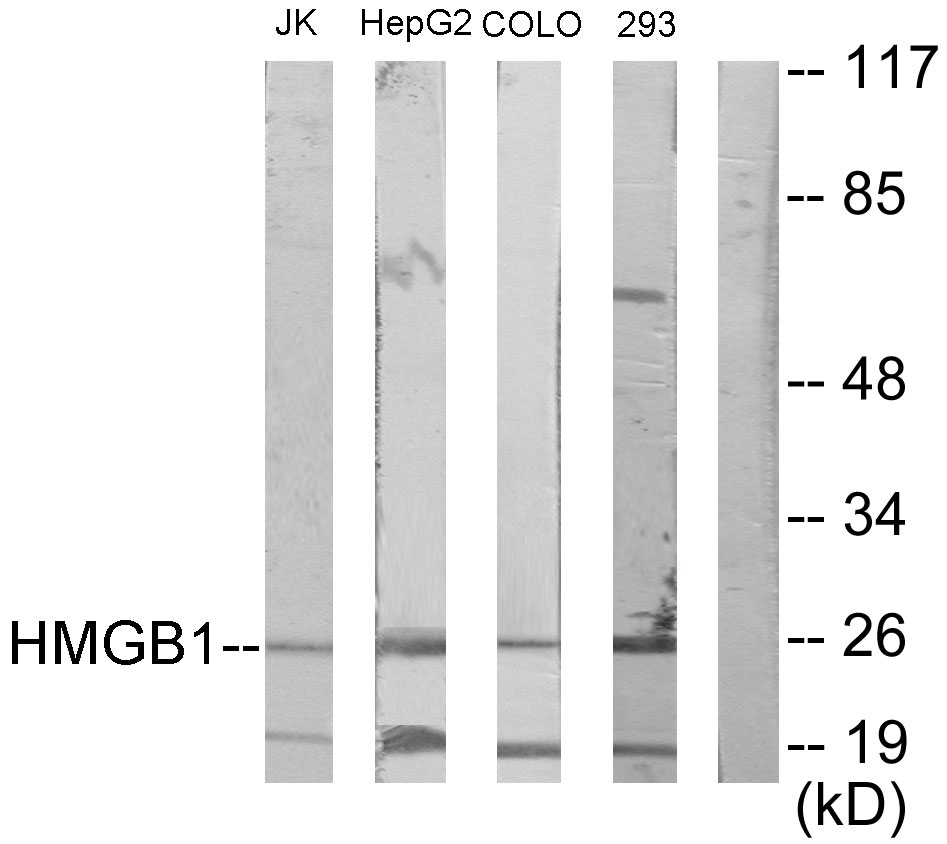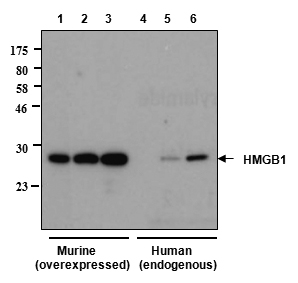
Western blot analysis of human and rat HMGB1 using anti-HMGB1, mAb (rec.) (GIBY-1-4) (Prod. No. AG-27B-0002) Different amounts of cell extracts from HEK293T cells (3microg, 5microg and 30microg) either transfected with a plasmid coding for rat HMGB1 (l
anti-HMGB1, mAb (rec.) (Giby-1-4)
AG-27B-0002
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetHMGB1
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product Nameanti-HMGB1, mAb (rec.) (Giby-1-4)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDGiby-1-4
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID3146
- Target nameHMGB1
- Target descriptionhigh mobility group box 1
- Target synonymsHMG-1, HMG1, HMG3, SBP-1, high mobility group protein B1, Amphoterin, Sulfoglucuronyl carbohydrate binding protein, high-mobility group (nonhistone chromosomal) protein 1
- HostHuman
- IsotypeIgG2
- Protein IDP09429
- Protein NameHigh mobility group protein B1
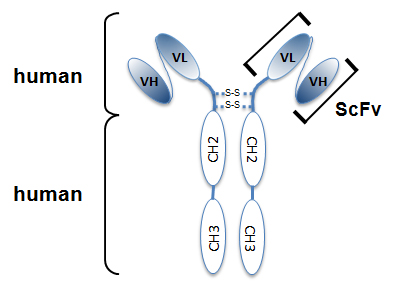
- Scientific DescriptionHMGB1 was originally discovered as an essential DNA-binding protein for regulating p53, NF-kappaB and other important proteins. It is secreted from activated dentric cells, macrophage and nectrotic cells, and acts as a ligand for RAGE, TLR-2 and TLR-4 expressed on surrounding cells. As a result, HMGB1 activates Rac, CDC42 and NF-kappaB inducing localized innate immunity of damaged tissue, tissue regeneration by recruitment of stem cells and hemostasis by induction of tissue factor expression. HMGB1 is also a causative agent of various diseases as it causes localized inflammation such as arteriosclerosis, chronic rheumatoid arthritis and nephritis. Anti-HMGB1, mAb (recombinant) (Giby-1-4) is an antibody developed by antibody phage display technology using a human naive antibody gene library. These libraries consist of scFv (single chain fragment variable) composed of VH (variable domain of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain) and VL (variable domain of the human immunoglobulin light chain) connected by a polypeptide linker. The antibody fragments are displayed on the surface of filamentous bacteriophage (M13). This scFv was selected by affinity selection on antigen in a process termed panning. Multiple rounds of panning are performed to enrich for antigen-specific scFv-phage. Monoclonal antibodies are subsequently identified by screening after each round of selection. The selected monoclonal scFv is cloned into an appropriate vector containing a Fc portion of interest and then produced in mammalian cells to generate an IgG like scFv-Fc fusion protein. - Recombinant Antibody. Recognizes human, mouse and rat HMGB1. Species cross-reactivity: Human, Mouse, Rat. Clone: Giby-1-4. Isotype: Human IgG2lambda. Applications: ELISA, WB. Host: Purified from HEK 293 cell culture supernatant. Liquid. In PBS containing 10% glycerol and 0.02% sodium azide. HMGB1 was originally discovered as an essential DNA-binding protein for regulating p53, NF-kappaB and other important proteins. It is secreted from activated dentric cells, macrophage and nectrotic cells, and acts as a ligand for RAGE, TLR-2 and TLR-4 expressed on surrounding cells. As a result, HMGB1 activates Rac, CDC42 and NF-kappaB inducing localized innate immunity of damaged tissue, tissue regeneration by recruitment of stem cells and hemostasis by induction of tissue factor expression. HMGB1 is also a causative agent of various diseases as it causes localized inflammation such as arteriosclerosis, chronic rheumatoid arthritis and nephritis. Anti-HMGB1, mAb (recombinant) (Giby-1-4) is an antibody developed by antibody phage display technology using a human naive antibody gene library. These libraries consist of scFv (single chain fragment variable) composed of VH (variable domain of the human immunoglobulin heavy chain) and VL (variable domain of the human immunoglobulin light chain) connected by a polypeptide linker. The antibody fragments are displayed on the surface of filamentous bacteriophage (M13). This scFv was selected by affinity selection on antigen in a process termed panning. Multiple rounds of panning are performed to enrich for antigen-specific scFv-phage. Monoclonal antibodies are subsequently identified by screening after each round of selection. The selected monoclonal scFv is cloned into an appropriate vector containing a Fc portion of interest and then produced in mammalian cells to generate an IgG like scFv-Fc fusion protein.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161