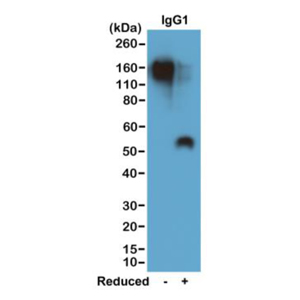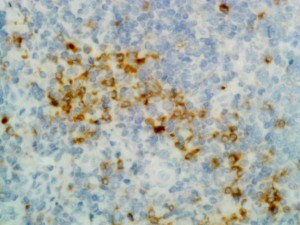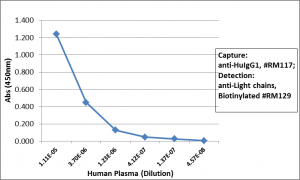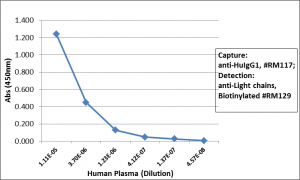
Sandwich ELISA using RM122 as the capture antibody (25ng/well), and Biotinylated anti-human light chains ( kappa+ lambda) antibody RM129 as the detection antibody, followed by an alkaline phosphatase conjugated streptavidin.
anti-IgG1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM117) (Biotin)
REV-31-1019-02
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-IgG1 (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM117) (Biotin)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ELISA, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM117
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateBiotin
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP01857
- Protein NameImmunoglobulin heavy constant gamma 1
- Scientific DescriptionIgG (Immunoglobulin G) is the most abundant Ig isotype in serum and makes up approximately 75% of all serum Immunoglobulins. In humans, there are four subclasses of IgG with highest serum concentrations of IgG1 followed by IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4. The IgG molecule consists of two heavy and two lights chains (kappa or lambda) resulting in a molecule with two arms for antigen binding. High levels of IgG antibodies are induced following the initial IgM response in a typical immune response to antigens. Because of its relative abundance and excellent specificity toward antigens, IgG is the principle antibody used in immunological research and clinical diagnostics. Clinically, measured IgG antibody levels are generally considered to be indicative of an individuals immune status to particular pathogens. This anti-human secondary antibody has well-characterized specificity for human IgG1 immunoglobulins and is useful in the detection, sorting or purification of its specified target. In general, secondary antibodies offer increased versatility enabling users to use many detection systems (e.g. HRP, AP, fluorescence). They can also provide greater sensitivity through signal amplification as multiple secondary antibodies can bind to a single primary antibody. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to the heavy chain of human IgG1. No cross reactivity with human IgG2, IgG3, IgG4, IgM, IgA, IgD, IgE, mouse IgG, rat IgG, or goat IgG. Applications: ICC, IHC, FACS, ELISA. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. IgG (Immunoglobulin G) is the most abundant Ig isotype in serum and makes up approximately 75% of all serum Immunoglobulins. In humans, there are four subclasses of IgG with highest serum concentrations of IgG1 followed by IgG2, IgG3 and IgG4. The IgG molecule consists of two heavy and two lights chains (kappa or lambda) resulting in a molecule with two arms for antigen binding. High levels of IgG antibodies are induced following the initial IgM response in a typical immune response to antigens. Because of its relative abundance and excellent specificity toward antigens, IgG is the principle antibody used in immunological research and clinical diagnostics. Clinically, measured IgG antibody levels are generally considered to be indicative of an individuals immune status to particular pathogens. This anti-human secondary antibody has well-characterized specificity for human IgG1 immunoglobulins and is useful in the detection, sorting or purification of its specified target. In general, secondary antibodies offer increased versatility enabling users to use many detection systems (e.g. HRP, AP, fluorescence). They can also provide greater sensitivity through signal amplification as multiple secondary antibodies can bind to a single primary antibody.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161