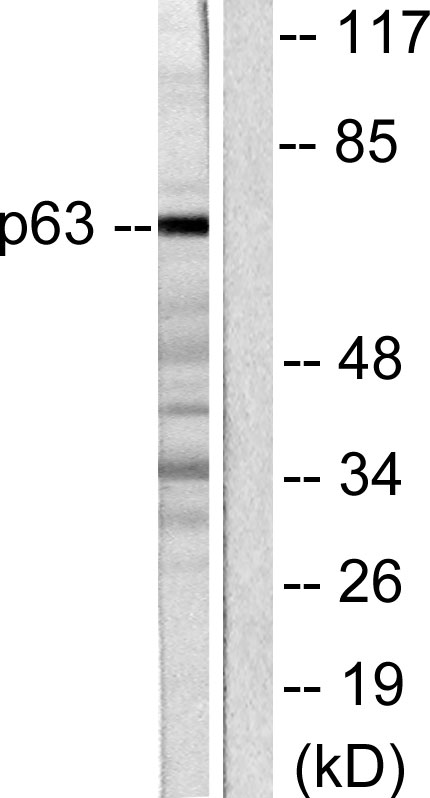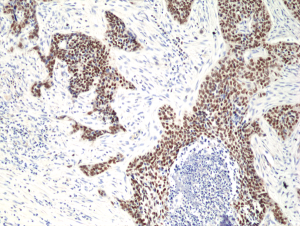
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human lung squamous carcinoma tissue section using anti-p40(DeltaNp63) rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM392) at a 1:50 dilution.
anti-p40 (deltaNp63) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM392)
REV-31-1278-00
ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetTP63
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-p40 (deltaNp63) (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM392)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM392
- Gene ID8626
- Target nameTP63
- Target descriptiontumor protein p63
- Target synonymsAIS, B(p51A), B(p51B), EEC3, KET, LMS, NBP, OFC8, RHS, SHFM4, TP53CP, TP53L, TP73L, p40, p51, p53CP, p63, p73H, p73L, tumor protein 63, amplified in squamous cell carcinoma, chronic ulcerative stomatitis protein, keratinocyte transcription factor KET, transformation-related protein 63, tumor protein p53-competing protein
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ9H3D4
- Protein NameTumor protein 63
- Scientific Descriptionp63 (TP63; Tumor protein 63) acts as a sequence-specific DNA binding transcriptional activator or repressor. The isoforms contain a varying set of transactivation and auto-regulating transactivation inhibiting domains thus showing an isoform-specific activity. p63 may be required in conjunction with TP73/p73 for initiation of p53/TP53 dependent apoptosis in response to genotoxic insults and the presence of activated oncogenes. It is involved in Notch signaling by inducing JAG1 and JAG2. p63 plays a role in the regulation of epithelial morphogenesis. p63 is required for limb formation from the apical ectodermal ridge. It also activates transcription of the p21 promoter. Mutations affecting the gene can result in acro-dermato-ungual-lacrimal-tooth syndrome, ankyloblepharon-ectodermal defects-cleft lip/palate, ectrodactyly ectodermal dysplasia, split-hand/foot malformation 4, limb-mammary syndrome, ectodermal dysplasia and orofacial cleft. p63 immunostaining has utility for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas, differentiating prostatic adenocarcinoma and benign prostatic tissue. p63 is also helpful in distinguishing poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma from small cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma. p63 should be strongly stained in poorly differentiated squamous cell, but negative in small cell or adenocarcinoma. Differentiating between lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma is an important distinction with therapeutic implications. Although the most frequently recommended squamous marker p63 is extremely sensitive, it suffers from low specificity due to its reactivity in a substantial proportion of lung adenocarcinomas and other tumor types, particularly lymphomas. p40 is a relatively unknown marker that recognizes DeltaNp63, a p63 isoform suggested to be highly specific for squamous/basal cells. p40 is equivalent to p63 in sensitivity for squamous cell carcinoma, but it is markedly superior to p63 in specificity, which eliminates a potential pitfall of misinterpreting a p63-positive adenocarcinoma or unsuspected lymphoma as squamous cell carcinoma. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human p40 (deltaNp63). Applications: IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. p63 (TP63; Tumor protein 63) acts as a sequence-specific DNA binding transcriptional activator or repressor. The isoforms contain a varying set of transactivation and auto-regulating transactivation inhibiting domains thus showing an isoform-specific activity. p63 may be required in conjunction with TP73/p73 for initiation of p53/TP53 dependent apoptosis in response to genotoxic insults and the presence of activated oncogenes. It is involved in Notch signaling by inducing JAG1 and JAG2. p63 plays a role in the regulation of epithelial morphogenesis. p63 is required for limb formation from the apical ectodermal ridge. It also activates transcription of the p21 promoter. Mutations affecting the gene can result in acro-dermato-ungual-lacrimal-tooth syndrome, ankyloblepharon-ectodermal defects-cleft lip/palate, ectrodactyly ectodermal dysplasia, split-hand/foot malformation 4, limb-mammary syndrome, ectodermal dysplasia and orofacial cleft. p63 immunostaining has utility for head and neck squamous cell carcinomas, differentiating prostatic adenocarcinoma and benign prostatic tissue. p63 is also helpful in distinguishing poorly differentiated squamous cell carcinoma from small cell carcinoma or adenocarcinoma. p63 should be strongly stained in poorly differentiated squamous cell, but negative in small cell or adenocarcinoma. Differentiating between lung adenocarcinoma and squamous cell carcinoma is an important distinction with therapeutic implications. Although the most frequently recommended squamous marker p63 is extremely sensitive, it suffers from low specificity due to its reactivity in a substantial proportion of lung adenocarcinomas and other tumor types, particularly lymphomas. p40 is a relatively unknown marker that recognizes DeltaNp63, a p63 isoform suggested to be highly specific for squamous/basal cells. p40 is equivalent to p63 in sensitivity for squamous cell carcinoma, but it is markedly superior to p63 in specificity, which eliminates a potential pitfall of misinterpreting a p63-positive adenocarcinoma or unsuspected lymphoma as squamous cell carcinoma.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161