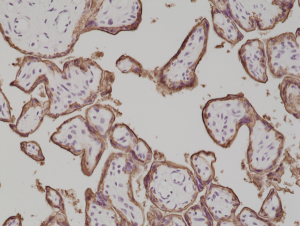
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human placenta tissue section using anti-PLAP rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM317) at a 1:1000 dilution.
anti-PLAP (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM317)
REV-31-1203-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetALPP
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-PLAP (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM317)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM317
- Gene ID250
- Target nameALPP
- Target descriptionalkaline phosphatase, placental
- Target synonymsALP, ALPI, IAP, PALP, PLAP, PLAP-1, alkaline phosphatase, placental type, Intestinal alkaline phosphatase, Intestinal-type alkaline phosphatase, alkaline phosphatase Regan isozyme, alkaline phosphomonoesterase, glycerophosphatase, placental alkaline phosphatase 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP05187
- Protein NameAlkaline phosphatase, placental type
- Scientific DescriptionPlacental Alkaline Phosphatase (PLAP) plays an important role in the regulation of specific inflammatory disease processes. There are at least four distinct but related alkaline phosphatases: intestinal, placental, placental-like and liver/bone/kidney. Placental Alkaline Phosphatase reacts with a membrane-bound isoenzyme (Regan and Nagao type). Placental Alkaline Phosphatase is useful in the identification of testicular germ cell tumors. Unlike germ cell tumors, PLAP-positive somatic cell tumors uniformly express epithelial membrane antigen (EMA). A proposed function of Placental Alkaline Phosphatase is matrix mineralization; however, mice that lack a functional form of this enzyme show normal skeletal development. Placental Alkaline Phosphatase has been linked directly to hypophosphatasia, a disorder that is characterized by hypercalcemia and includes skeletal defects. The character of hypophosphatasia can vary, however, depending on the specific mutation since this determines age of onset and severity of symptoms. - Recombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human PLAP (Placental alkaline phosphatase). Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Placental Alkaline Phosphatase (PLAP) plays an important role in the regulation of specific inflammatory disease processes. There are at least four distinct but related alkaline phosphatases: intestinal, placental, placental-like and liver/bone/kidney. Placental Alkaline Phosphatase reacts with a membrane-bound isoenzyme (Regan and Nagao type). Placental Alkaline Phosphatase is useful in the identification of testicular germ cell tumors. Unlike germ cell tumors, PLAP-positive somatic cell tumors uniformly express epithelial membrane antigen (EMA). A proposed function of Placental Alkaline Phosphatase is matrix mineralization; however, mice that lack a functional form of this enzyme show normal skeletal development. Placental Alkaline Phosphatase has been linked directly to hypophosphatasia, a disorder that is characterized by hypercalcemia and includes skeletal defects. The character of hypophosphatasia can vary, however, depending on the specific mutation since this determines age of onset and severity of symptoms.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

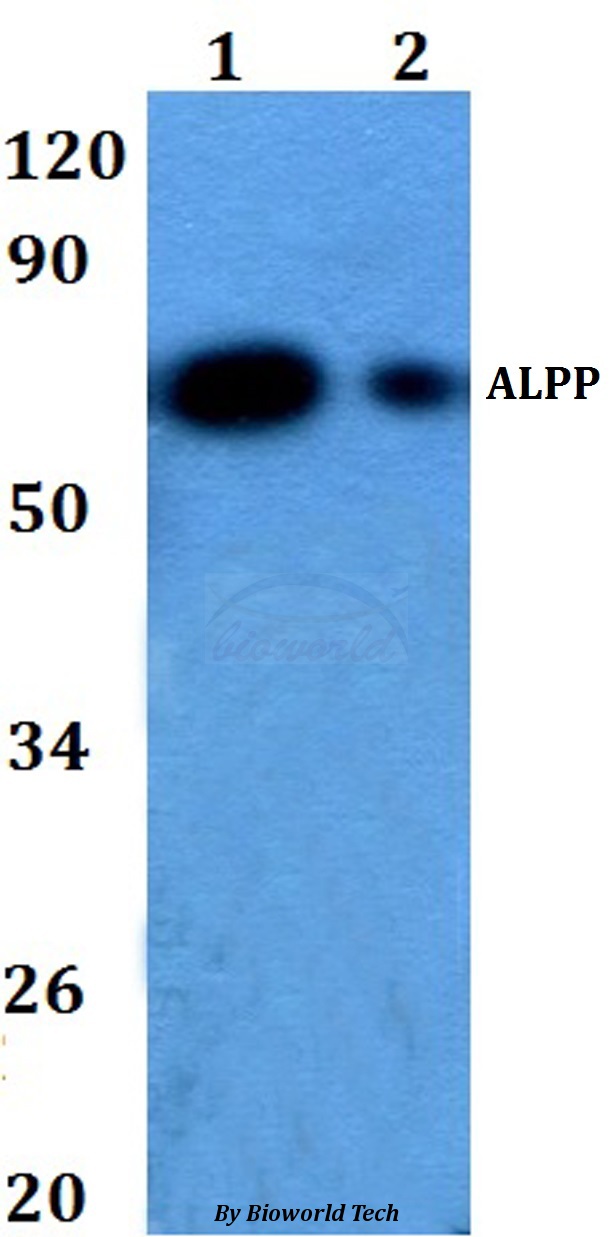


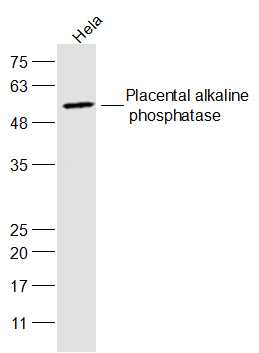

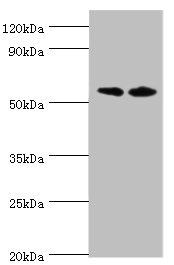
![IHC-P analysis of human placenta (mature) tissue using GTX04413 Placental Alkaline Phosphatase antibody [MSVA-350R] HistoMAX?. Placental Alkaline Phosphatase immunostaining increases continuously throughout the pregnancy. Placental Alkaline Phosphatase immunostaining is strong in the cyto- and syncytiotrophoblast of the mature placenta.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX04413/GTX04413_20230728_IHC-P_98_23072722_473.webp)
