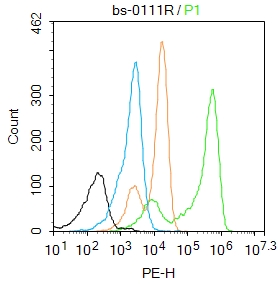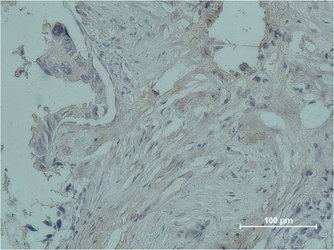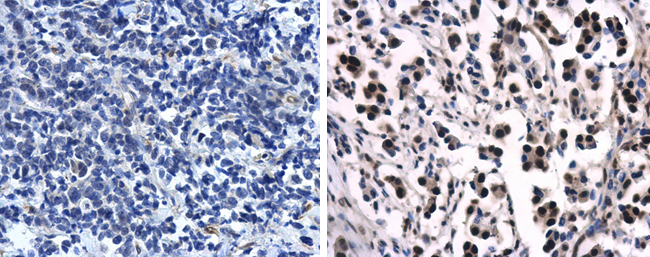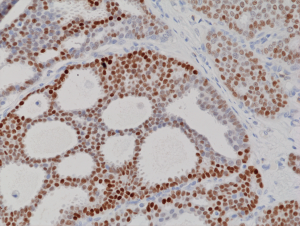
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human breast cancer tissue sections using Anti-Progesterone Receptor (PR) Rabbit Monoclonal Antibody (Clone RM357) at a 1:100 dilution.
anti-Progesterone Receptor (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM357)
REV-31-1243-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetPGR
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Progesterone Receptor (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM357)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM357
- Gene ID5241
- Target namePGR
- Target descriptionprogesterone receptor
- Target synonymsNR3C3, PR, progesterone receptor, nuclear receptor subfamily 3 group C member 3
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP06401
- Protein NameProgesterone receptor
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Progesterone Receptor (PR). It may also react to mouse and rat PR, as predicted by immunogen homology. Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. The progesterone receptor (PR) is a member of the steroid family of nuclear receptors. The PR mediates the physiological effects of progesterone, which plays a central role in reproductive events associated with the establishment and maintenance of pregnancy. PR is found as a 94 kDa protein (Form A) or a 120 kDa protein (Form B) due to the use of alternative translation initiation sites. PR-B is the transcriptionally active form and is responsible for activating genes for the maintenance of the endometrium, maintenance of pregnancy and inhibition of ovulation. PR-A is identical to PR-B except for a 165 amino acid deletion at the N-terminus. This deletion exposes a 140 amino acid inhibitory domain (ID) that acts as a repressor of steroid hormone transcriptional activity. In its inactive state, PgR forms a multiprotein complex which includes heat shock proteins and immunophins. Upon binding of progesterone hormone to its receptor, there is a conformational change that allows dimerization and binding of the receptor to progesterone response elements (PRE) sequences, resulting in activated transcription. A Null mutation in the PGR gene leads to pleiotrophic reproductive abnormalities. - The progesterone receptor (PR) is a member of the steroid family of nuclear receptors. The PR mediates the physiological effects of progesterone, which plays a central role in reproductive events associated with the establishment and maintenance of pregnancy. PR is found as a 94 kDa protein (Form A) or a 120 kDa protein (Form B) due to the use of alternative translation initiation sites. PR-B is the transcriptionally active form and is responsible for activating genes for the maintenance of the endometrium, maintenance of pregnancy and inhibition of ovulation. PR-A is identical to PR-B except for a 165 amino acid deletion at the N-terminus. This deletion exposes a 140 amino acid inhibitory domain (ID) that acts as a repressor of steroid hormone transcriptional activity. In its inactive state, PgR forms a multiprotein complex which includes heat shock proteins and immunophins. Upon binding of progesterone hormone to its receptor, there is a conformational change that allows dimerization and binding of the receptor to progesterone response elements (PRE) sequences, resulting in activated transcription. A Null mutation in the PGR gene leads to pleiotrophic reproductive abnormalities.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161