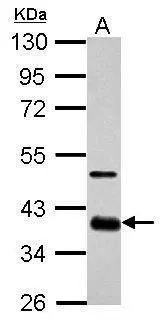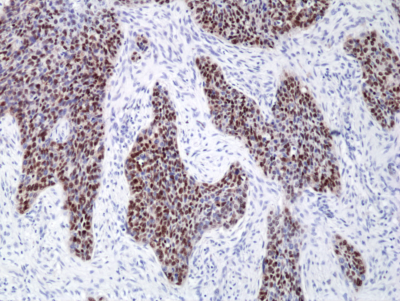
anti-Sox2 Rabbit Monoclonal (RM427)
REV-31-1314-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetSOX2
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Sox2 Rabbit Monoclonal (RM427)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM427
- Gene ID6657
- Target nameSOX2
- Target descriptionSRY-box transcription factor 2
- Target synonymsANOP3, MCOPS3, transcription factor SOX-2, SRY (sex determining region Y)-box 2, SRY-box 2, SRY-related HMG-box gene 2, sex determining region Y-box 2, transcription factor SOX2
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP48431
- Protein NameTranscription factor SOX-2
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody RM427 reacts to human SOX2. Application: IHC, WB. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. SOX2 is the most studied member of SRY-related box transcription factor family. It binds to target genes through its highly conserved HMG box domain. Inactivation of the SOX2 gene causes lethality during embryonic development. SOX2 knockdown in embryonic stem cells results in their differentiation. Co-expression of SOX with OCT4, MYC, and KLF4 is sufficient to reprogram somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which exert similar characteristics as natural pluripotent stem cells. These findings indicate that SOX2 is crucial for the self-renewal and pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. In addition, over-expression of SOX2 has been found in various types of malignant cancer. Knockdown of SOX2 results in cell cycle arrest by downregulating cyclin D1 and inhibition of tumor cell proliferation, suggesting that SOX2 is involved in activating genes associated with tumor progression. - SOX2 is the most studied member of SRY-related box transcription factor family. It binds to target genes through its highly conserved HMG box domain. Inactivation of the SOX2 gene causes lethality during embryonic development. SOX2 knockdown in embryonic stem cells results in their differentiation. Co-expression of SOX with OCT4, MYC, and KLF4 is sufficient to reprogram somatic cells to induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs), which exert similar characteristics as natural pluripotent stem cells. These findings indicate that SOX2 is crucial for the self-renewal and pluripotency of embryonic stem cells. In addition, over-expression of SOX2 has been found in various types of malignant cancer. Knockdown of SOX2 results in cell cycle arrest by downregulating cyclin D1 and inhibition of tumor cell proliferation, suggesting that SOX2 is involved in activating genes associated with tumor progression.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161