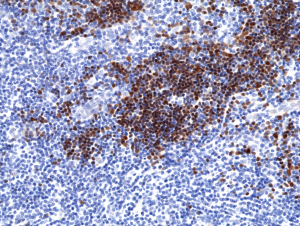
Immunohistochemical staining of formalin fixed and paraffin embedded human thymus tissue section using anti-TdT rabbit monoclonal antibody (Clone RM379) at a 1:200 dilution.
anti-Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM379)
REV-31-1265-00
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetDNTT
Overview
- SupplierRevMAb Biosciences
- Product Nameanti-Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (human), Rabbit Monoclonal (RM379)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDRM379
- Gene ID1791
- Target nameDNTT
- Target descriptionDNA nucleotidylexotransferase
- Target synonymsTDT, DNA nucleotidylexotransferase, nucleosidetriphosphate:DNA deoxynucleotidylexotransferase, terminal addition enzyme, terminal deoxynucleotidyltransferase, terminal deoxyribonucleotidyltransferase, terminal transferase
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP04053
- Protein NameDNA nucleotidylexotransferase
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant Antibody. This antibody reacts to human Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (TdT). Applications: WB, IHC. Source: Rabbit. Liquid. 50% Glycerol/PBS with 1% BSA and 0.09% sodium azide. Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT) is a DNA polymerase located in the cell nucleus which catalyzes the polymerization of deoxynucleotides at the 3 hydroxyl ends of oligo or polydeoxynucleotide initiators and functions without a template. TdT adds N-nucleotides to the V, D, and J exons of the TCR and BCR genes during antibody gene recombination, enabling the phenomenon of junctional diversity. The diversity introduced by TdT has played an important role in the evolution of the vertebrate immune system, significantly increasing the variety of antigen receptors that a cell is equipped with to fight pathogens. TdT is expressed in immature, pre-B, pre-T lymphoid cells and acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma cells. TdT is considered to be a highly specific marker for the diagnosis and classification of acute lymphoblastic lymphoma/leuksemias. The determination of TdT expression is most valuable when it is difficult to differentiate histologically between lymphoblastic lymphoma and Burkitts lymphoma. - Terminal Deoxynucleotidyl Transferase (TdT) is a DNA polymerase located in the cell nucleus which catalyzes the polymerization of deoxynucleotides at the 3 hydroxyl ends of oligo or polydeoxynucleotide initiators and functions without a template. TdT adds N-nucleotides to the V, D, and J exons of the TCR and BCR genes during antibody gene recombination, enabling the phenomenon of junctional diversity. The diversity introduced by TdT has played an important role in the evolution of the vertebrate immune system, significantly increasing the variety of antigen receptors that a cell is equipped with to fight pathogens. TdT is expressed in immature, pre-B, pre-T lymphoid cells and acute lymphoblastic leukemia/lymphoma cells. TdT is considered to be a highly specific marker for the diagnosis and classification of acute lymphoblastic lymphoma/leuksemias. The determination of TdT expression is most valuable when it is difficult to differentiate histologically between lymphoblastic lymphoma and Burkitts lymphoma.
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161


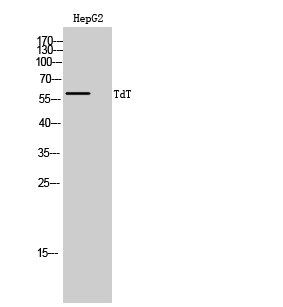


![TdT antibody [C1C3] detects TdT protein by western blot analysis. A. 30 μg Jurkat whole cell extract B. 30 μg Jurkat nuclear extract 7.5 % SDS-PAGE TdT antibody [C1C3] (GTX108697) dilution: 1:500](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX108697/GTX108697_41577_WB_Fraction_w_23060120_366.webp)
