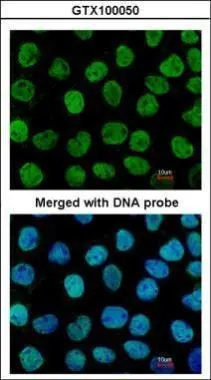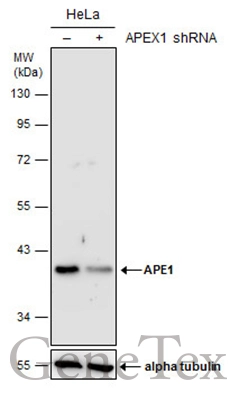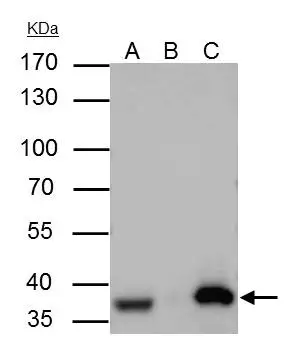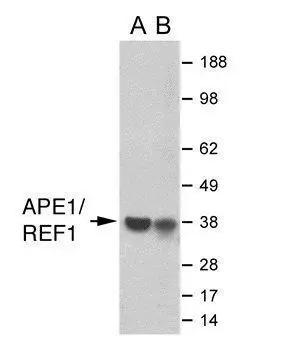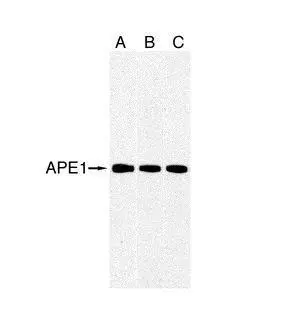
GTX70131 at a 1/1000 dilution staining ~ 38 kDa APE 1 in 35mg of: A) HepG2 whole cell lysate; B) HeLa whole cell lysate; C) Raji whole cell lysate.
APE1 antibody [2104]
GTX70131
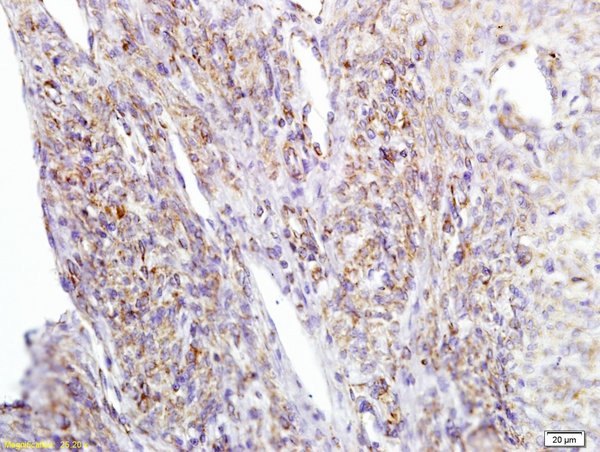
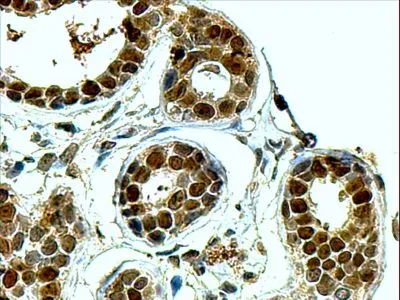
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetAPEX1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameAPE1 antibody [2104]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000. IHC-P: 1:5000. ELISA: 1:1000-1:10000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID2104
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID328
- Target nameAPEX1
- Target descriptionapurinic/apyrimidinic endodeoxyribonuclease 1
- Target synonymsAPE, APE1, APEN, APEX, APX, HAP1, REF1, DNA repair nuclease/redox regulator APEX1, AP endonuclease class I, AP lyase, APEX nuclease (multifunctional DNA repair enzyme) 1, DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) endonuclease, DNA-(apurinic or apyrimidinic site) lyase, apurinic-apyrimidinic endonuclease 1, apurinic/apyrimidinic (abasic) endonuclease, deoxyribonuclease (apurinic or apyrimidinic), protein REF-1, redox factor-1
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP27695
- Protein NameDNA repair nuclease/redox regulator APEX1
- Scientific DescriptionApurinic/apyrimidinic (AP) sites occur frequently in DNA molecules by spontaneous hydrolysis, by DNA damaging agents or by DNA glycosylases that remove specific abnormal bases. AP sites are pre-mutagenic lesions that can prevent normal DNA replication so the cell contains systems to identify and repair such sites. Class II AP endonucleases cleave the phosphodiester backbone 5 to the AP site. This gene encodes the major AP endonuclease in human cells. Splice variants have been found for this gene; all encode the same protein. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Guo Z, Zheng L, Dai H, et al. Human DNA polymerase beta polymorphism, Arg137Gln, impairs its polymerase activity and interaction with PCNA and the cellular base excision repair capacity. Nucleic Acids Res. 2009,37(10):3431-41. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkp201Read this paper