Arginase I (human) (rec.) (highly active)
AG-40T-0124
Protein IDP05089
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameArginase I (human) (rec.) (highly active)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration0.2 ug/ul
- Estimated Purity>90%
- Gene ID383
- Target nameARG1
- Target descriptionarginase 1
- Target synonymsarginase-1, arginase, liver, liver-type arginase, type I arginase
- Protein IDP05089
- Protein NameArginase-1
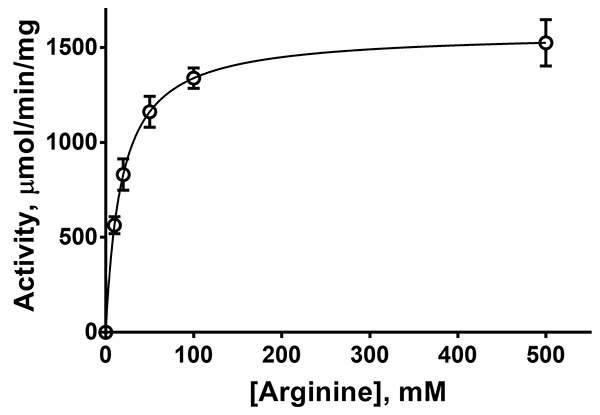
- Scientific DescriptionArginase catalyzes the hydrolysis of arginine to ornithine and urea. At least two isoforms of mammalian arginase exist (types I and II) which differ in their tissue distribution, subcellular localization, immunologic crossreactivity and physiologic function. The type I isoform is a cytosolic enzyme and expressed predominantly in the liver as a component of the urea cycle. Inherited deficiency of this enzyme results in argininemia, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by hyperammonemia. Arginase is involved in the nitric oxide (NO) pathway and immune cell arginine metabolism. It is fundamentally involved in cancer, inflammation, infections, fibrotic diseases, neurobiology, pregnancy and immune regulation in general. - Protein. Full length human arginase I. Source: E. coli. Liquid. In 10mM TRIS-HCl, pH 7.5, containing 1mM beta-mercaptoethanol, 1mM MnCl2 and 50% glycerol. Purity: >90% (SDS-PAGE). Arginase catalyzes the hydrolysis of arginine to ornithine and urea. At least two isoforms of mammalian arginase exist (types I and II) which differ in their tissue distribution, subcellular localization, immunologic crossreactivity and physiologic function. The type I isoform is a cytosolic enzyme and expressed predominantly in the liver as a component of the urea cycle. Inherited deficiency of this enzyme results in argininemia, an autosomal recessive disorder characterized by hyperammonemia. Arginase is involved in the nitric oxide (NO) pathway and immune cell arginine metabolism. It is fundamentally involved in cancer, inflammation, infections, fibrotic diseases, neurobiology, pregnancy and immune regulation in general.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,-80°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman