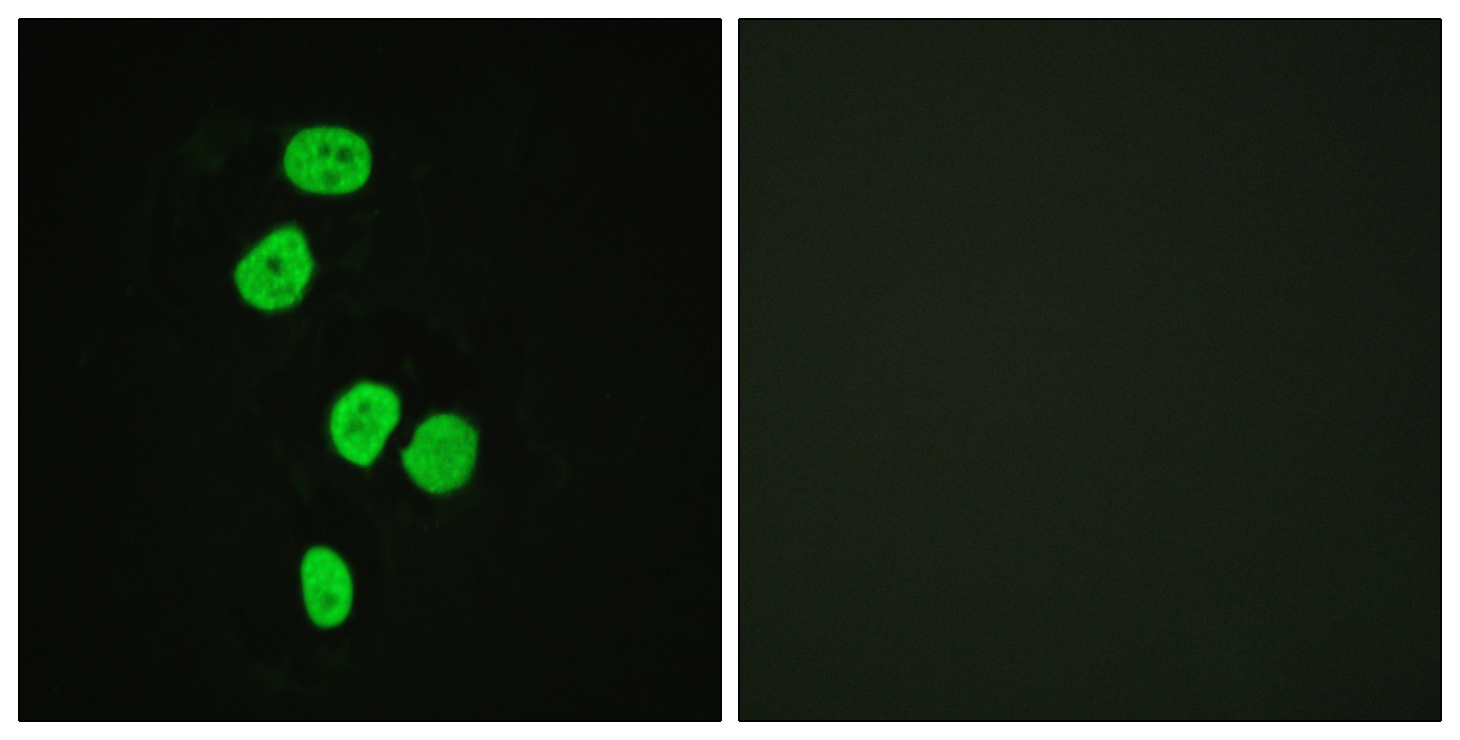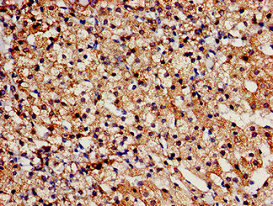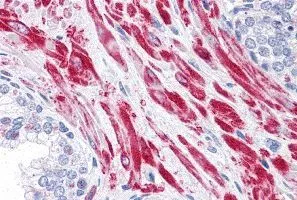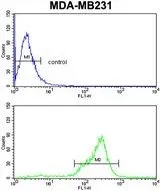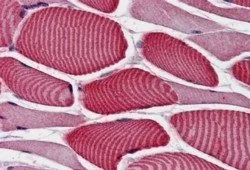
IHC-P analysis of human skeletal muscle using GTX89152 AS160 / TBC1D4 antibody, Internal. Antigen retrieval : citrate buffer pH 6 Dilution : 3.8μg/ml
AS160 / TBC1D4 antibody, Internal
GTX89152
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetTBC1D4
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameAS160 / TBC1D4 antibody, Internal
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 0.1-0.3microg/ml. IHC-P: 3-5microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.50 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID9882
- Target nameTBC1D4
- Target descriptionTBC1 domain family member 4
- Target synonymsAS160, NIDDM5, TBC1 domain family member 4, TBC (Tre-2, BUB2, CDC16) domain-containing protein, akt substrate of 160 kDa
- HostGoat
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDO60343
- Protein NameTBC1 domain family member 4
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene is a member of the Tre-2/BUB2/CDC16 domain family. The protein encoded by this gene is a Rab-GTPase-activating protein, and contains two phopshotyrosine-binding domains (PTB1 and PTB2), a calmodulin-binding domain (CBD), a Rab-GTPase domain, and multiple AKT phosphomotifs. This protein is thought to play an important role in glucose homeostasis by regulating the insulin-dependent trafficking of the glucose transporter 4 (GLUT4), important for removing glucose from the bloodstream into skeletal muscle and fat tissues. Reduced expression of this gene results in an increase in GLUT4 levels at the plasma membrane, suggesting that this protein is important in intracellular retention of GLUT4 under basal conditions. When exposed to insulin, this protein is phosphorylated, dissociates from GLUT4 vesicles, resulting in increased GLUT4 at the cell surface, and enhanced glucose transport. Phosphorylation of this protein by AKT is required for proper translocation of GLUT4 to the cell surface. Individuals homozygous for a mutation in this gene are at higher risk for type 2 diabetes and have higher levels of circulating glucose and insulin levels after glucose ingestion. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Aug 2015]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161