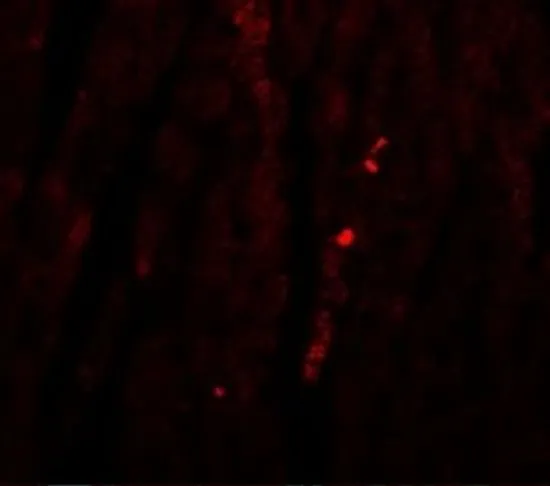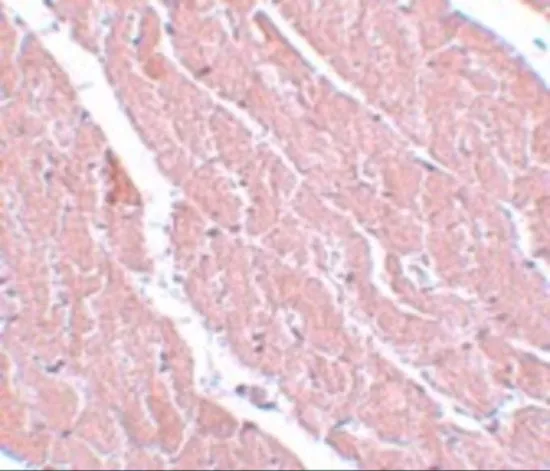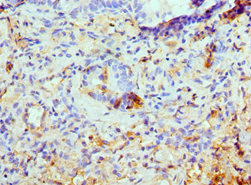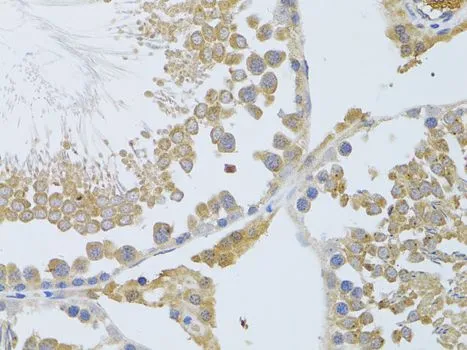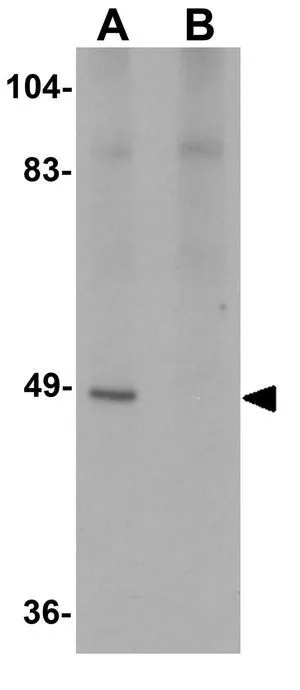
WB analysis of rat heart tissue lysate in (A) the absence and (B) the presence of blocking peptide using GTX85183 ATG13 antibody. Working concentration : 1 μg/ml
ATG13 antibody
GTX85183
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetATG13
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameATG13 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1 microg/mL. IHC-P: 5 microg/mL. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID9776
- Target nameATG13
- Target descriptionautophagy related 13
- Target synonymsKIAA0652, PARATARG8, autophagy-related protein 13, ATG13 autophagy related 13 homolog
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDO75143
- Protein NameAutophagy-related protein 13
- Scientific DescriptionAutophagy, the process of bulk degradation of cellular proteins through an autophagosomic-lysosomal pathway is important for normal growth control and may be defective in tumor cells. It is involved in the preservation of cellular nutrients under starvation conditions as well as the normal turnover of cytosolic components. This process is negatively regulated by TOR (Target of rapamycin) through phosphorylation of autophagy protein ATG1. ATG13 forms a complex with ULK1 and ULK2, the mammalian homologs of ATG1, and with FIP200. This complex is a target of TOR phosphorylation under normal conditions; inhibition of TOR by rapamycin or leucine deprivation leads to dephosphorylation of ATG13, ULK1 and ULK2, which then leads to autophagy. Knockdown of ATG13 inhibits autophagosome formation.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Autophagy control by the VEGF-C/NRP-2 axis in cancer and its implication for treatment resistance. Stanton MJ et al., 2013 Jan 1, Cancer ResRead this paper