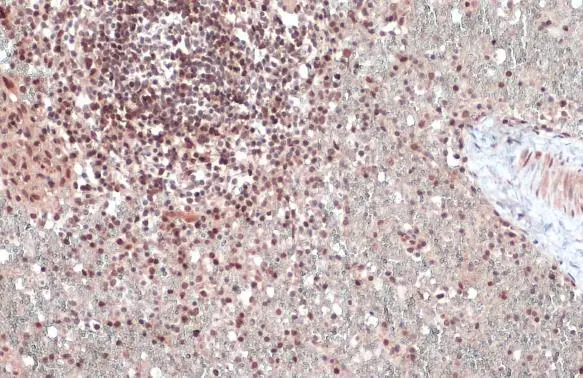
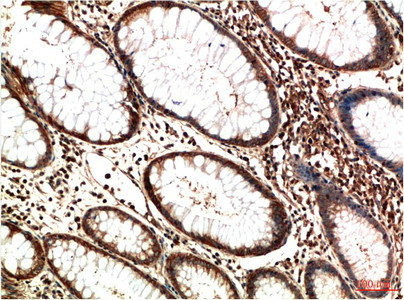
ATM antibody detects ATM protein at nucleus by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded cat spleen. ATM stained by ATM antibody (GTX111106) diluted at 1:500. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min
ATM antibody
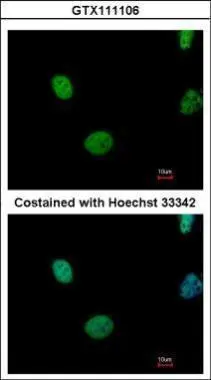
GTX111106
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityFeline, Human
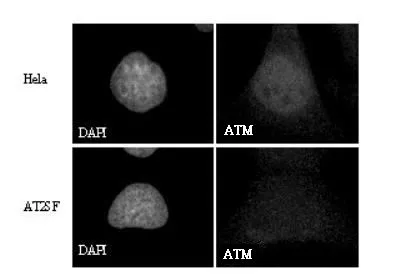
TargetATM
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameATM antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.93 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID472
- Target nameATM
- Target descriptionATM serine/threonine kinase
- Target synonymsAT1, ATA, ATC, ATD, ATDC, ATE, TEL1, TELO1, serine-protein kinase ATM, A-T mutated, AT mutated, TEL1, telomere maintenance 1, homolog, ataxia telangiectasia mutated, serine/threonine kinase ATM
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ13315
- Protein NameSerine-protein kinase ATM
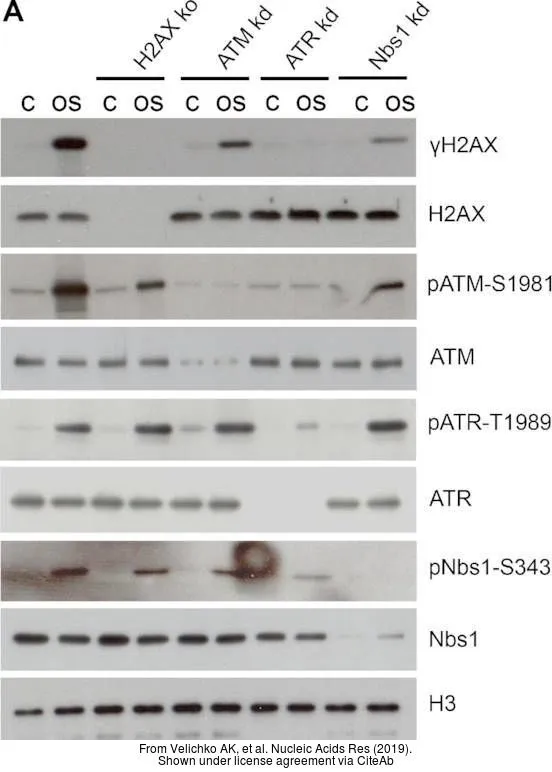
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene belongs to the PI3/PI4-kinase family. This protein is an important cell cycle checkpoint kinase that phosphorylates; thus, it functions as a regulator of a wide variety of downstream proteins, including tumor suppressor proteins p53 and BRCA1, checkpoint kinase CHK2, checkpoint proteins RAD17 and RAD9, and DNA repair protein NBS1. This protein and the closely related kinase ATR are thought to be master controllers of cell cycle checkpoint signaling pathways that are required for cell response to DNA damage and for genome stability. Mutations in this gene are associated with ataxia telangiectasia, an autosomal recessive disorder. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityFeline, Human
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

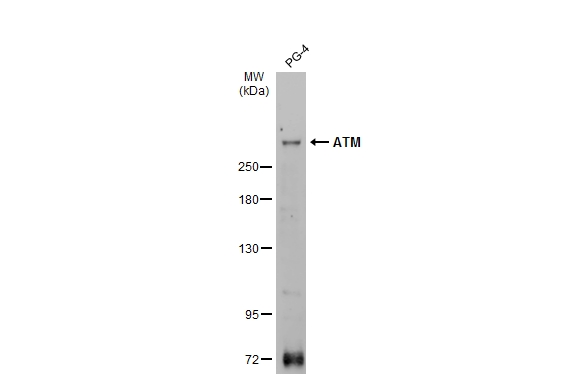
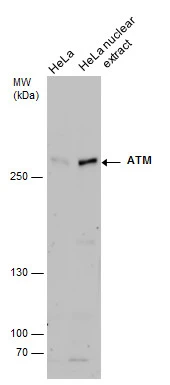
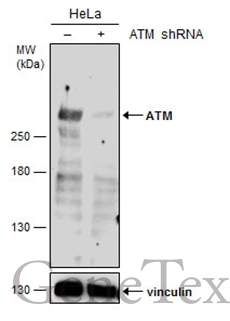



![IHC-P analysis of mouse spleen tissue using GTX30636 ATM (phospho Ser1981) antibody [10H11.E12].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX30636/GTX30636_329_IHC-P_w_23060722_410.webp)
![IHC-P analysis of human colon carcinoma tissue using GTX34046 ATM antibody [1D1]. Dilution : 1:200](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX34046/GTX34046_20200622_IHC-P_298_w_23060801_692.webp)
![IHC-P analysis of human breast carcinoma tissue using GTX34047 ATM antibody [4G9]. Dilution : 1:200](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX34047/GTX34047_20200622_IHC-P_269_w_23060801_385.webp)
![IHC-P analysis of human breast carcinoma tissue using GTX34048 ATM antibody [3D3]. Dilution : 1:200](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX34048/GTX34048_20200622_IHC-P_270_w_23060801_426.webp)