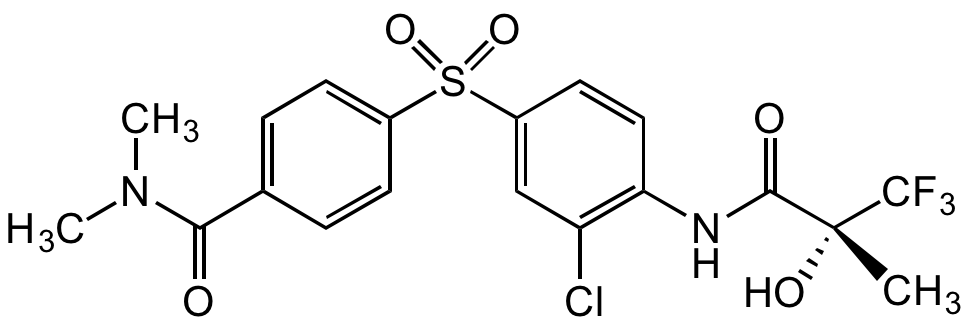
Chemical Structure
AZD 7545 [252017-04-2]
AG-CR1-3692
CAS Number252017-04-2
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight478.9
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameAZD 7545 [252017-04-2]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number252017-04-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC19H18ClF3N2O5S
- Molecular Weight478.9
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 252017-04-2. Formula: C19H18ClF3N2O5S. MW: 478.9. . Potent and selective pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 2 (PDK2) inhibitor (IC50=6.4nM), consequently increasing pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) activity. Less potent inhibitor towards PDK1 and PDK3 (IC50=87 and 600nM, respectively). Inhibitor of glycolysis. Antiobesity and antidiabetic agent. Improves blood glucose control in obese (fa/fa) Zucker rats. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. To maintain a continuous and steady supply of ATP during the feed-fast cycle, cells must select fatty acid or glucose for fuel. This process is largely controlled by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC), which regulates the entry of glycolytic products into the tricarboxylic acid cycle by catalyzing the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) in the mitochondria of mammalian cells. PDKs and pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatases (PDPs) are key regulators of PDC activity, and they act in a phosphorylation-dephosphorylation manner. - Potent and selective pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase 2 (PDK2) inhibitor (IC50=6.4nM), consequently increasing pyruvate dehydrogenase (PDH) activity. Less potent inhibitor towards PDK1 and PDK3 (IC50=87 and 600nM, respectively). Inhibitor of glycolysis. Antiobesity and antidiabetic agent. Improves blood glucose control in obese (fa/fa) Zucker rats. Useful agent for immunometabolism research. To maintain a continuous and steady supply of ATP during the feed-fast cycle, cells must select fatty acid or glucose for fuel. This process is largely controlled by the pyruvate dehydrogenase complex (PDC), which regulates the entry of glycolytic products into the tricarboxylic acid cycle by catalyzing the oxidative decarboxylation of pyruvate to acetyl-coenzyme A (CoA) in the mitochondria of mammalian cells. PDKs and pyruvate dehydrogenase phosphatases (PDPs) are key regulators of PDC activity, and they act in a phosphorylation-dephosphorylation manner.
- SMILESO=C(N(C)C)C1=CC=C(S(C2=CC(Cl)=C(NC([C@](O)(C)C(F)(F)F)=O)C=C2)(=O)=O)C=C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![AZD7545 [252017-04-2]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/77/CgoaEGayH_KERY7KAAAAAHLdrHg859.png)