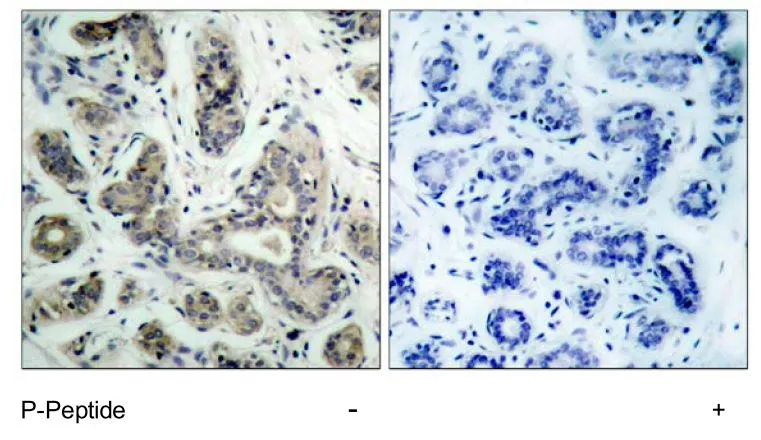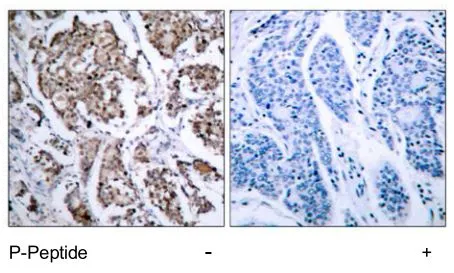
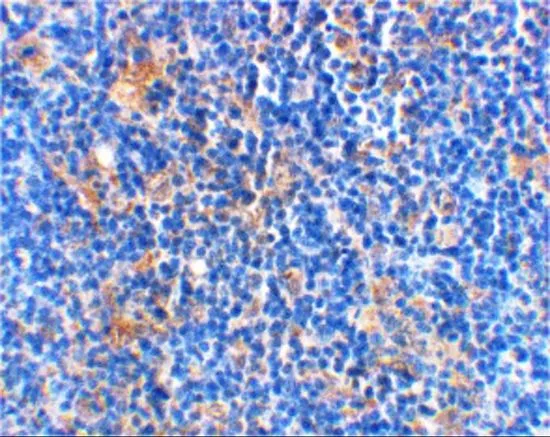
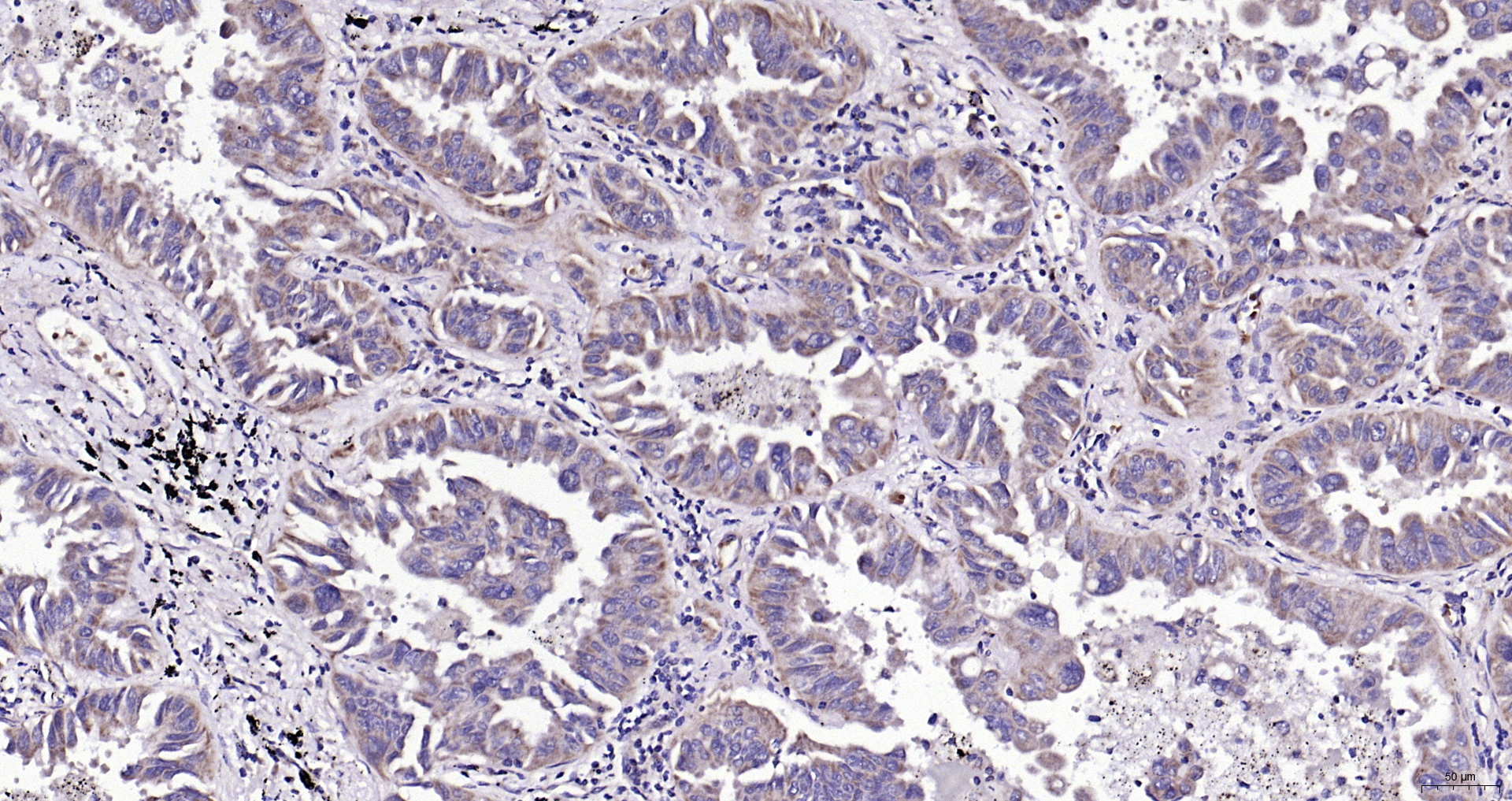
IHC-P analysis of rat thymus tissue using GTX31688 Bad antibody. Working concentration : 10 μg/ml
Bad antibody
GTX31688
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetBAD
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameBad antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 0.5 - 2 microg/mL. IHC-P: 2 microg/mL. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID572
- Target nameBAD
- Target descriptionBCL2 associated agonist of cell death
- Target synonymsBBC2, BCL2L8, bcl2-associated agonist of cell death, BCL-X/BCL-2 binding protein, BCL2-antagonist of cell death protein, BCL2-binding component 6, BCL2-binding protein, bcl-2-binding component 6, bcl-2-like protein 8, bcl-XL/Bcl-2-associated death promoter, bcl2 antagonist of cell death, bcl2-L-8
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ92934
- Protein NameBcl2-associated agonist of cell death
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a member of the BCL-2 family. BCL-2 family members are known to be regulators of programmed cell death. This protein positively regulates cell apoptosis by forming heterodimers with BCL-xL and BCL-2, and reversing their death repressor activity. Proapoptotic activity of this protein is regulated through its phosphorylation. Protein kinases AKT and MAP kinase, as well as protein phosphatase calcineurin were found to be involved in the regulation of this protein. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants which encode the same isoform. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- mTOR Inhibitors Can Enhance the Anti-Tumor Effects of DNA Vaccines through Modulating Dendritic Cell Function in the Tumor Microenvironment. Chen YL et al., 2019 May 2, Cancers (Basel)Read this paper

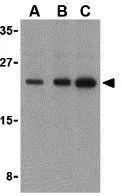
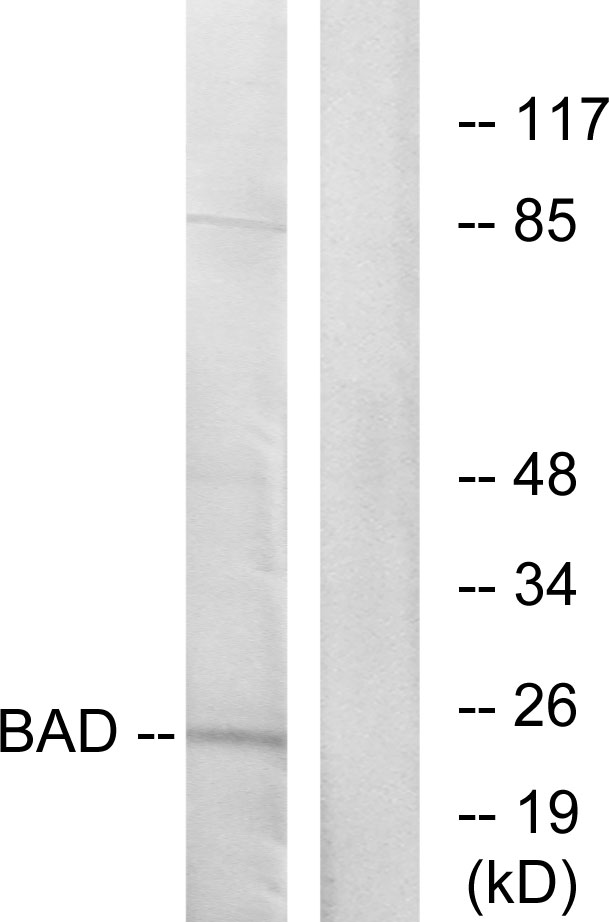





![Various whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 15% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Bad antibody [GT1175] (GTX09508) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX09508/GTX09508_4000000074_20200410_WB_w_23053123_409.webp)