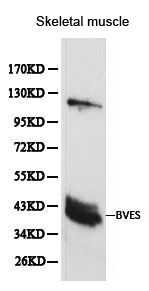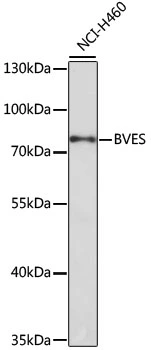
WB analysis of NCI-H460 cell lysate using GTX30098 BVES antibody. Dilution : 1:1000 Loading : 25μg per lane
BVES antibody
GTX30098
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetPOPDC1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameBVES antibody
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID11149
- Target namePOPDC1
- Target descriptionpopeye domain cAMP effector 1
- Target synonymsBVES, CARICK, HBVES, LGMD2X, LGMDR25, POP1, popeye domain-containing protein 1, blood vessel epicardial substance
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ8NE79
- Protein NamePopeye domain-containing protein 1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a member of the POP family of proteins containing three putative transmembrane domains. This gene is expressed in cardiac and skeletal muscle and may play an important role in development of these tissues. The mouse ortholog may be involved in the regeneration of adult skeletal muscle and may act as a cell adhesion molecule in coronary vasculogenesis. Three transcript variants encoding the same protein have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Dec 2010]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Inhibition of Musashi-1 enhances chemotherapeutic sensitivity in gastric cancer patient-derived xenografts.Read this paper