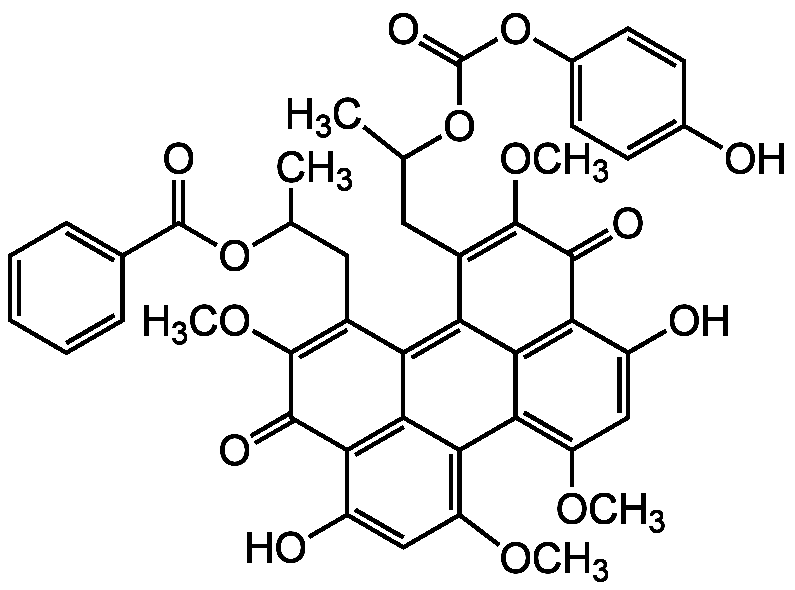
Chemical Structure
Calphostin C [121263-19-2] [121263-19-2]
AG-CN2-0430
CAS Number121263-19-2
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>95%
Molecular Weight790.8
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameCalphostin C [121263-19-2] [121263-19-2]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number121263-19-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Molecular FormulaC44H38O14
- Molecular Weight790.8
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 121263-19-2. Formula: C44H38O14. MW: 790.8. Isolated from Cladosporium cladosporioides sp. Potent and highly specific cell permeable protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor. The inhibition of PKC is light-dependent. PKA, PKG, DAG kinase, phospholipase D1 and D2, myosin light chain kinase and c-Src inhibitor. Anticancer compound. Inhibits cell proliferation and strongly induces apoptosis in vitro. Inducer of endoplasmic reticulum ER-stress. Shown to directly and potently block L-type Ca channels. Calphostin C specifically inhibits contraction-stimulated glucose transport but not insulin-stimulated glucose transport in skeletal muscle. Wnt/beta-catenin/lef-1 signaling inhibitor. beta-catenin/TCF antagonist. Inhibits Wnt-activated genes in a dose-dependent fashion - Potent and highly specific cell permeable protein kinase C (PKC) inhibitor [1]. The inhibition of PKC is light-dependent. PKA, PKG, DAG kinase, phospholipase D1 and D2, myosin light chain kinase and c-Src inhibitor. Anticancer compound. Inhibits cell proliferation and strongly induces apoptosis in vitro. Inducer of endoplasmic reticulum ER-stress. Shown to directly and potently block L-type Ca channels. Calphostin C specifically inhibits contraction-stimulated glucose transport but not insulin-stimulated glucose transport in skeletal muscle. Wnt/beta-catenin/lef-1 signaling inhibitor. beta-catenin/TCF antagonist. Inhibits Wnt-activated genes in a dose-dependent fashion
- SMILESCOC1=C2C3=C(OC)C=C(O)C4=C3C(C(CC(C)OC(=O)C3=CC=CC=C3)=C(OC)C4=O)=C3C(CC(C)OC(=O)OC4=CC=C(O)C=C4)=C(OC)C(=O)C(C(O)=C1)=C23
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Calphostin C [121263-19-2] [121263-19-2]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/69/CgoaEWY7LR2EJp1NAAAAAMuGbNc690.png)