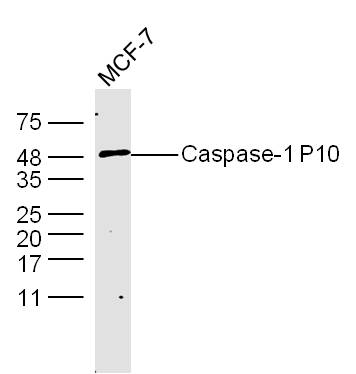
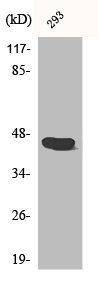
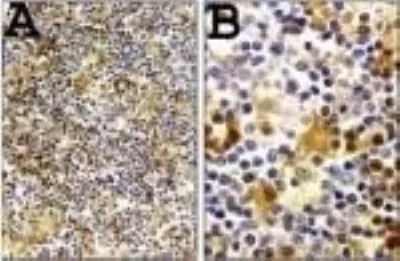
![WB analysis of HeLa (A) and NIH-3T3 (B) cell lysate using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 0.5 μg/ml and 2 μg/ml WB analysis of HeLa (A) and NIH-3T3 (B) cell lysate using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 0.5 μg/ml and 2 μg/ml](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX14367/GTX14367_1077_WB_w_23060620_226.webp)
WB analysis of HeLa (A) and NIH-3T3 (B) cell lysate using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 0.5 μg/ml and 2 μg/ml
Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]
GTX14367
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCASP1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCaspase 1 antibody [14F468]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 0.5 - 2 microg/ml. IHC-P: 1:10 - 1:500. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID14F468
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID834
- Target nameCASP1
- Target descriptioncaspase 1
- Target synonymsICE, IL1BC, P45, caspase-1, IL-1 beta-converting enzyme, IL1B-convertase, caspase 1, apoptosis-related cysteine peptidase, interleukin 1, beta, convertase, interleukin 1-B converting enzyme
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP29466
- Protein NameCaspase-1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a protein which is a member of the cysteine-aspartic acid protease (caspase) family. Sequential activation of caspases plays a central role in the execution-phase of cell apoptosis. Caspases exist as inactive proenzymes which undergo proteolytic processing at conserved aspartic residues to produce 2 subunits, large and small, that dimerize to form the active enzyme. This gene was identified by its ability to proteolytically cleave and activate the inactive precursor of interleukin-1, a cytokine involved in the processes such as inflammation, septic shock, and wound healing. This gene has been shown to induce cell apoptosis and may function in various developmental stages. Studies of a similar gene in mouse suggest a role in the pathogenesis of Huntington disease. Alternative splicing of this gene results in five transcript variants encoding distinct isoforms. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Fu Y, Yuan J, Sang F, et al. Biejiajian Pill Ameliorates Diabetes-Associated Atherosclerosis through Inhibition of the NLRP3 Inflammasome. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2022,2022:9131178. doi: 10.1155/2022/9131178Read this paper
- Qin Y, Li Q, Liang W, et al. TRIM28 SUMOylates and stabilizes NLRP3 to facilitate inflammasome activation. Nat Commun. 2021,12(1):4794. doi: 10.1038/s41467-021-25033-4Read this paper
- Deng J, Tan W, Luo Q, et al. Long Non-coding RNA MEG3 Promotes Renal Tubular Epithelial Cell Pyroptosis by Regulating the miR-18a-3p/GSDMD Pathway in Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Acute Kidney Injury. Front Physiol. 2021,12:663216. doi: 10.3389/fphys.2021.663216Read this paper
- Song H, Zhao C, Yu Z, et al. UAF1 deubiquitinase complexes facilitate NLRP3 inflammasome activation by promoting NLRP3 expression. Nat Commun. 2020,11(1):6042. doi: 10.1038/s41467-020-19939-8Read this paper
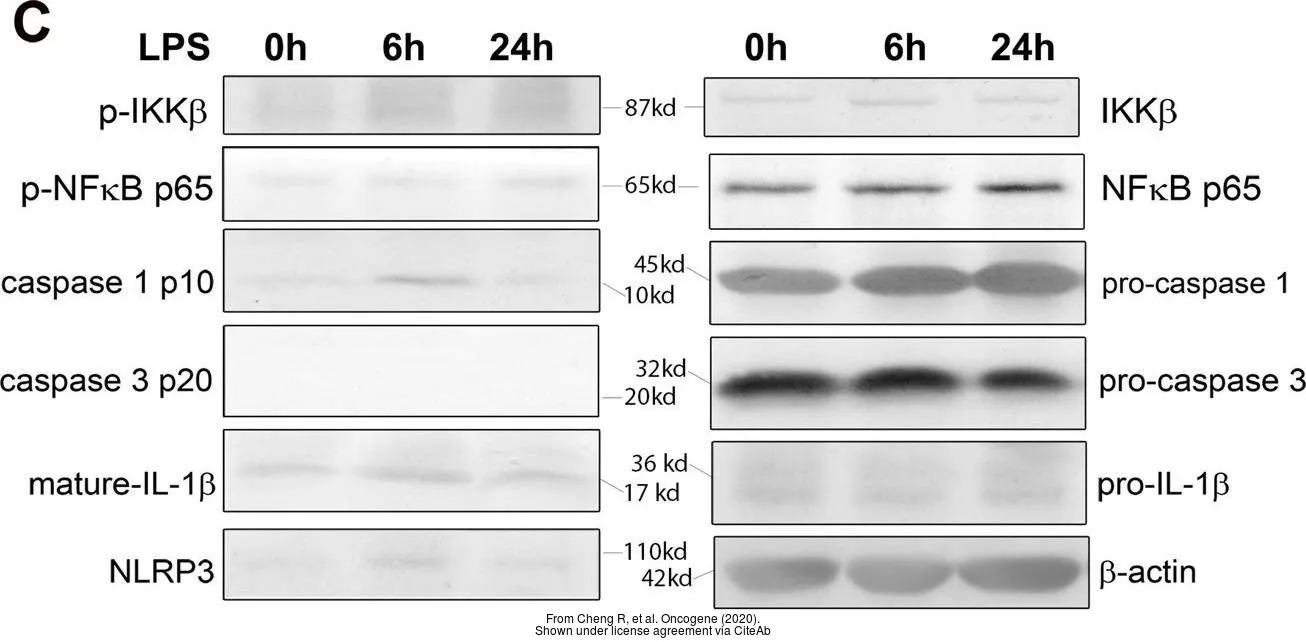
- Cheng R, Billet S, Liu C, et al. Periodontal inflammation recruits distant metastatic breast cancer cells by increasing myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Oncogene. 2020,39(7):1543-1556. doi: 10.1038/s41388-019-1084-zRead this paper
- Haldar S, Dru C, Mishra R, et al. Histone deacetylase inhibitors mediate DNA damage repair in ameliorating hemorrhagic cystitis. Sci Rep. 2016,6:39257. doi: 10.1038/srep39257Read this paper
- Kolb R, Phan L, Borcherding N, et al. Obesity-associated NLRC4 inflammasome activation drives breast cancer progression. Nat Commun. 2016,7:13007. doi: 10.1038/ncomms13007Read this paper

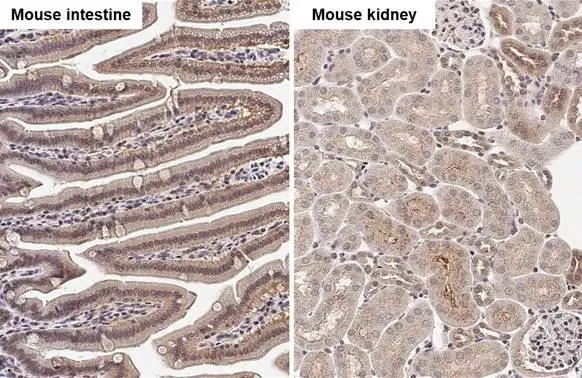
![IHC-P analysis of human ovarian carcinoma tissue using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 5 μg/ml IHC-P analysis of human ovarian carcinoma tissue using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 5 μg/ml](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX14367/GTX14367_446_IHC-P_w_23060620_681.webp)
![IHC-P analysis of human lung tissue using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 5 μg/ml IHC-P analysis of human lung tissue using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 5 μg/ml](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX14367/GTX14367_445_IHC-P_w_23060620_797.webp)
![IHC-P analysis of human rectum adenocarcinoma tissue using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 5 μg/ml Antigen retrieval : 10 mM sodium citrate buffer, pH 6.0 IHC-P analysis of human rectum adenocarcinoma tissue using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 5 μg/ml Antigen retrieval : 10 mM sodium citrate buffer, pH 6.0](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX14367/GTX14367_447_IHC-P_w_23060620_418.webp)
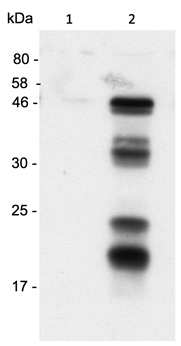
![WB analysis of HeLa cell lysate using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. WB analysis of HeLa cell lysate using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX14367/GTX14367_1078_WB_w_23060620_127.webp)
![IHC-P analysis of human colon tissue using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 5 μg/ml IHC-P analysis of human colon tissue using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 5 μg/ml](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX14367/GTX14367_444_IHC-P_w_23060620_802.webp)
![IHC-P analysis of human skin tissue using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 5 μg/ml IHC-P analysis of human skin tissue using GTX14367 Caspase 1 antibody [14F468]. Dilution : 5 μg/ml](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX14367/GTX14367_448_IHC-P_w_23060620_774.webp)