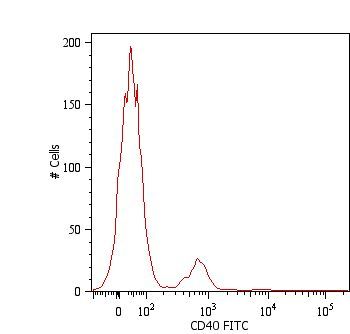
![FACS analysis of U2OS cells using GTX18028 CD40 antibody [C40/2383]. Blue : Primary antibody Red : Isotype control FACS analysis of U2OS cells using GTX18028 CD40 antibody [C40/2383]. Blue : Primary antibody Red : Isotype control](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX18028/GTX18028_20200115_FACS_1907_w_23060620_500.webp)
FACS analysis of U2OS cells using GTX18028 CD40 antibody [C40/2383]. Blue : Primary antibody Red : Isotype control
CD40 antibody [C40/2383]
GTX18028
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
Product group Antibodies
TargetCD40
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCD40 antibody [C40/2383]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC-P: 1-2microg/ml for 30 minutes at RT. FACS: 1-2microg/106 cells. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin, Other Application
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDC40/2383
- Concentration0.2 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID958
- Target nameCD40
- Target descriptionCD40 molecule
- Target synonymsBp50, CDW40, TNFRSF5, p50, tumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5, B cell surface antigen CD40, B cell-associated molecule, CD40 molecule, TNF receptor superfamily member 5, CD40L receptor
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2b
- Protein IDP25942
- Protein NameTumor necrosis factor receptor superfamily member 5
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene is a member of the TNF-receptor superfamily. The encoded protein is a receptor on antigen-presenting cells of the immune system and is essential for mediating a broad variety of immune and inflammatory responses including T cell-dependent immunoglobulin class switching, memory B cell development, and germinal center formation. AT-hook transcription factor AKNA is reported to coordinately regulate the expression of this receptor and its ligand, which may be important for homotypic cell interactions. Adaptor protein TNFR2 interacts with this receptor and serves as a mediator of the signal transduction. The interaction of this receptor and its ligand is found to be necessary for amyloid-beta-induced microglial activation, and thus is thought to be an early event in Alzheimer disease pathogenesis. Mutations affecting this gene are the cause of autosomal recessive hyper-IgM immunodeficiency type 3 (HIGM3). Multiple alternatively spliced transcript variants of this gene encoding distinct isoforms have been reported. [provided by RefSeq, Nov 2014]
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203

![IHC-P analysis of human tonsil tissue using GTX18028 CD40 antibody [C40/2383]. IHC-P analysis of human tonsil tissue using GTX18028 CD40 antibody [C40/2383].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX18028/GTX18028_20200115_IHC-P_1312_w_23060620_718.webp)
![ICC/IF analysis of MCF-7 cells using GTX00854 CD40 antibody [5C3] (FITC). Fixation : 4% PFA Permeabilization : 0.25% Triton X-100 Dilution : 1:20](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX00854/GTX00854_20200406_AP_002_141_w_23053121_667.webp)
![ICC/IF analysis of MCF-7 cells using GTX00875 CD40 antibody [5C3]. Fixation : 4% PFA Permeabilization : 0.25% Triton X-100 Dilution : 1:100](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX00875/GTX00875_20200406_AP_002_139_w_23053121_219.webp)
![ICC/IF analysis of human peripheral blood lymphocyles (left) and mouse L1210 cells (right) using GTX83365 CD40 antibody [9G10]. Green : CD40 Blue: DRAQ5 fluorescent DNA dye](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX83365/GTX83365_20170912_ICCIF_w_23061322_421.webp)