CD40L (mouse) (multimeric) (rec.) (Biotin)
AG-40B-0020B
Protein IDP27548
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameCD40L (mouse) (multimeric) (rec.) (Biotin)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration0.1 mg/ml
- ConjugateBiotin
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID21947
- Target nameCd40lg
- Target descriptionCD40 ligand
- Target synonymsCD154, CD40-L, Cd40l, HIGM1, IGM, IMD3, Ly-62, Ly62, T-BAM, TRAP, Tnfsf5, Tnlg8b, gp39, CD40 ligand, T-cell antigen Gp39, TNF-related activation protein, tumor necrosis factor ligand 8b, tumor necrosis factor ligand superfamily member 5
- Protein IDP27548
- Protein NameCD40 ligand
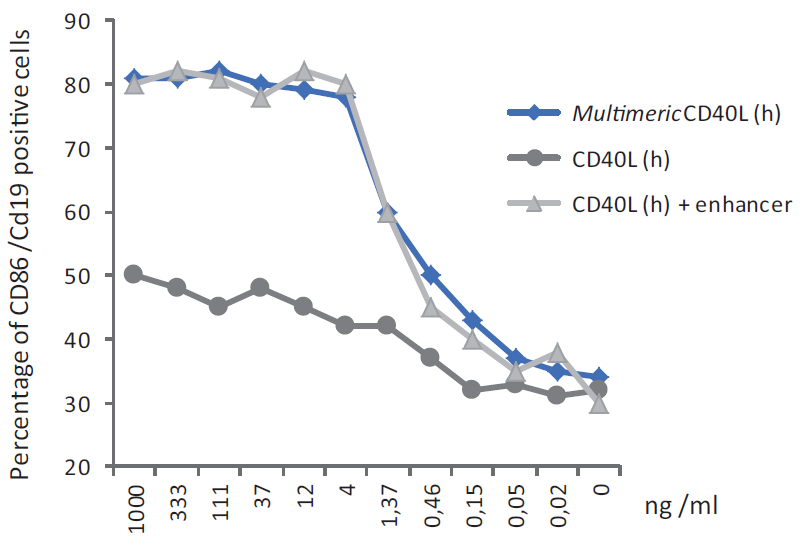
- Scientific DescriptionRecombinant protein. Mouse CD40L (aa 115-260) is fused at the N-terminus to mouse ACRP30headless (aa 18-111) and a FLAG®-tag. Binds to human and mouse CD40. Endotoxin: <0.05EU/microg purified protein (LAL test; Lonza). Lyophilized. Contains PBS. The costimulatory molecule CD40, a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily, critically regulates B cell and T cell function in adaptive immunity and inflammation by interacting with CD40L (CD154). CD40L mediates a range of activities on B cells, including induction of activation-associated surface antigen, entry into cell cycle, isotype switching, immunoglobulin secretion and memory generation. CD40-CD40L interaction also plays important roles in monocyte activation and DC maturation. MultimericCD40L™ is a high activity construct in which two trimeric CD40 ligands are artificially linked via the collagen domain of ACRP30. This construct very effectively simulates the natural membrane-assisted aggregation of CD40L in vivo. It provides a simple and equally potent alternative to CD40L+enhancer combinations. MultimericCD40L™ has shown to suppress alum-induced IL-1beta release and caspase-1 activation in a dose-, CD40- and time dependent manner, without affecting BMDM (bone marrow-derived macrophages) viability. It also effectively suppressed the inflammasome function triggered by NLRP3 activators. The secretion of caspase-1 independent inflammatory mediators has been shown to be unaltered or even enhanced. MultimericCD40L™ enhances B cell proliferation. - The costimulatory molecule CD40, a member of the tumor necrosis factor (TNF) receptor superfamily, critically regulates B cell and T cell function in adaptive immunity and inflammation by interacting with CD40L (CD154). CD40L mediates a range of activities on B cells, including induction of activation-associated surface antigen, entry into cell cycle, isotype switching, immunoglobulin secretion and memory generation. CD40-CD40L interaction also plays important roles in monocyte activation and DC maturation. MultimericCD40L™ is a high activity construct in which two trimeric CD40 ligands are artificially linked via the collagen domain of ACRP30. This construct very effectively simulates the natural membrane-assisted aggregation of CD40L in vivo. It provides a simple and equally potent alternative to CD40L+enhancer combinations. MultimericCD40L™ has shown to suppress alum-induced IL-1beta release and caspase-1 activation in a dose-, CD40- and time dependent manner, without affecting BMDM (bone marrow-derived macrophages) viability. It also effectively suppressed the inflammasome function triggered by NLRP3 activators. The secretion of caspase-1 independent inflammatory mediators has been shown to be unaltered or even enhanced. MultimericCD40L™ enhances B cell proliferation.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesMouse