CD66b antibody [80H3]
GTX75908
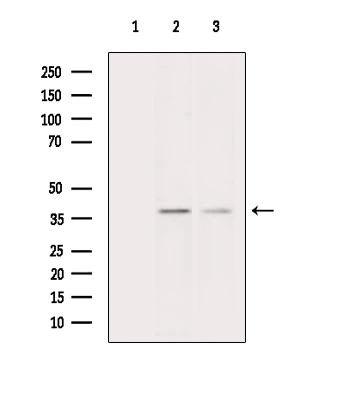
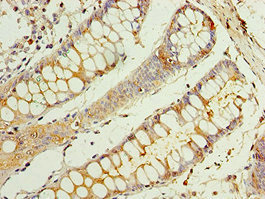
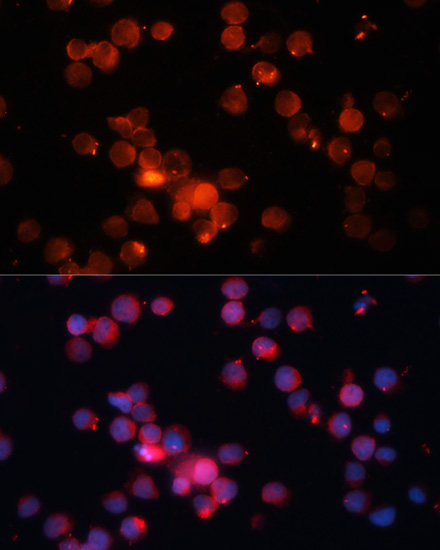
ApplicationsFunctional Assay, Flow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCEACAM8
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCD66b antibody [80H3]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC-Fr: 1/25-1/100. FACS: 1/50-1/100. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFunctional Assay, Flow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Frozen
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID80H3
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1088
- Target nameCEACAM8
- Target descriptionCEA cell adhesion molecule 8
- Target synonymsCD66b, CD67, CGM6, NCA-95, cell adhesion molecule CEACAM8, CD67 antigen, carcinoembryonic antigen CGM6, carcinoembryonic antigen gene family member 6, carcinoembryonic antigen related cell adhesion molecule 8, non-specific cross-reacting antigen NCA-95
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP31997
- Protein NameCell adhesion molecule CEACAM8
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Yu Y, Gool E, Berckmans RJ, et al. Extracellular vesicles from human saliva promote hemostasis by delivering coagulant tissue factor to activated platelets. J Thromb Haemost. 2018,16(6):1153-1163. doi: 10.1111/jth.14023Read this paper
- Eken C, Sadallah S, Martin PJ, et al. Ectosomes of polymorphonuclear neutrophils activate multiple signaling pathways in macrophages. Immunobiology. 2013,218(3):382-92. doi: 10.1016/j.imbio.2012.05.021Read this paper
- Eken C, Martin PJ, Sadallah S, et al. Ectosomes released by polymorphonuclear neutrophils induce a MerTK-dependent anti-inflammatory pathway in macrophages. J Biol Chem. 2010,285(51):39914-21. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.126748Read this paper