![IHC-P analysis of human tonsil tissue using GTX73643 CD68 antibody [KP1]. IHC-P analysis of human tonsil tissue using GTX73643 CD68 antibody [KP1].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX73643/GTX73643_20191203_IHC-P_181_w_23061322_279.webp)
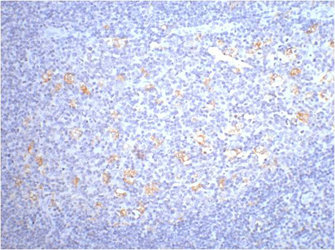
IHC-P analysis of human tonsil tissue using GTX73643 CD68 antibody [KP1].
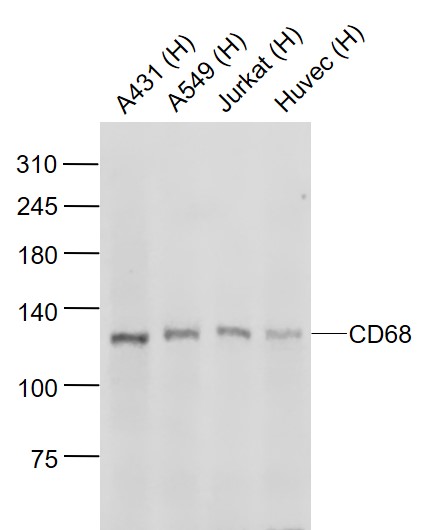
CD68 antibody [KP1]
GTX73643
ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCD68
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCD68 antibody [KP1]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteIHC-P: 1:50-1:100. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDKP1
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID968
- Target nameCD68
- Target descriptionCD68 molecule
- Target synonymsGP110, LAMP4, SCARD1, macrosialin, CD68 antigen, macrophage antigen CD68, scavenger receptor class D, member 1
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP34810
- Protein NameMacrosialin
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a 110-kD transmembrane glycoprotein that is highly expressed by human monocytes and tissue macrophages. It is a member of the lysosomal/endosomal-associated membrane glycoprotein (LAMP) family. The protein primarily localizes to lysosomes and endosomes with a smaller fraction circulating to the cell surface. It is a type I integral membrane protein with a heavily glycosylated extracellular domain and binds to tissue- and organ-specific lectins or selectins. The protein is also a member of the scavenger receptor family. Scavenger receptors typically function to clear cellular debris, promote phagocytosis, and mediate the recruitment and activation of macrophages. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcripts encoding different isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Wu Y, Li F, Wang Y, et al. Lipid-lowering treatment in a rabbit model of atherosclerosis: a vessel wall magnetic resonance imaging study. Ann Transl Med. 2022,10(10):569. doi: 10.21037/atm-22-1263Read this paper