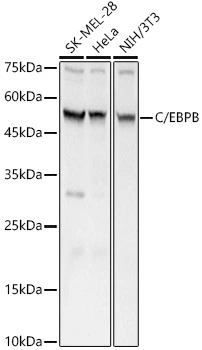
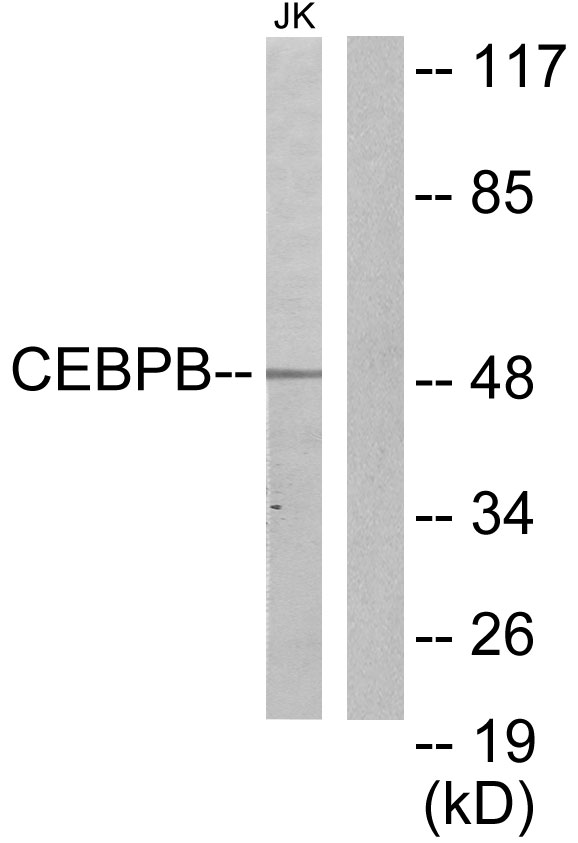
WB analysis of various sample lysates using GTX64382 C/EBP beta antibody. Dilution : 1:700 Loading : 25μg per lane
C/EBP beta antibody
GTX64382
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCEBPB
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameC/EBP beta antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:1000. IHC-P: 1:20 - 1:100. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1051
- Target nameCEBPB
- Target descriptionCCAAT enhancer binding protein beta
- Target synonymsC/EBP-beta, IL6DBP, NF-IL6, TCF5, CCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta, CCAAT/enhancer binding protein (C/EBP), beta, interleukin 6-dependent DNA-binding protein, nuclear factor NF-IL6, nuclear factor of interleukin 6, transcription factor 5, transcription factor C/EBP beta
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP17676
- Protein NameCCAAT/enhancer-binding protein beta
- Scientific DescriptionThis intronless gene encodes a transcription factor that contains a basic leucine zipper (bZIP) domain. The encoded protein functions as a homodimer but can also form heterodimers with CCAAT/enhancer-binding proteins alpha, delta, and gamma. Activity of this protein is important in the regulation of genes involved in immune and inflammatory responses, among other processes. The use of alternative in-frame AUG start codons results in multiple protein isoforms, each with distinct biological functions. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2013]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Pigment epithelium-derived factor inhibits adipogenesis in 3T3-L1 adipocytes and protects against high-fat diet-induced obesity and metabolic disorders in mice. Chen CC et al., 2019 Aug, Transl ResRead this paper





![C/EBP beta antibody [21A1]](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX70283/NFIL6-antibody-21A1-GTX70283-IHC-1_w_23061221_704.webp)