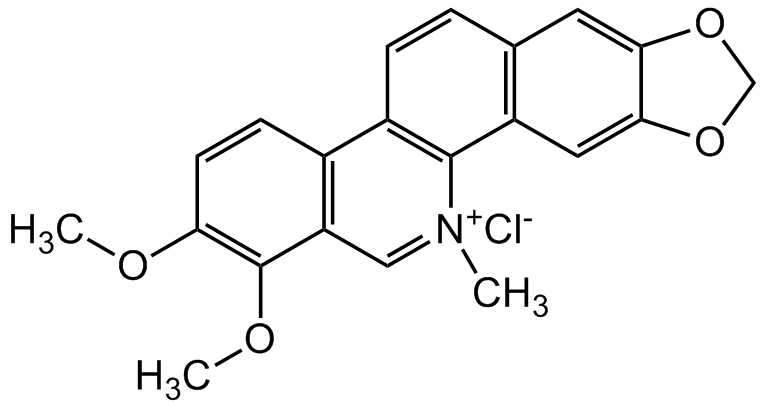
Chemical Structure
Chelerythrine chloride
AG-CR1-0071
CAS Number3895-92-9
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight383.8
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameChelerythrine chloride
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number3895-92-9
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC21H18ClNO4
- Molecular Weight383.8
- Scientific DescriptionCell permeable potent inhibitor of protein kinase C. Does not inhibit tyrosine protein kinases, cAMP-dependent protein kinase or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase [1, 5]. Antiplatelet, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antitumor compound [1, 2, 9, 12, 15]. Apoptosis inducer in cancer cells in vitro and in vivo [3, 9]. Activates MAPK and JUNK signaling pathways [4, 8]. Affects translocation of PKC from cytosol to plasma membrane [6]. Neurite outgrowth stimulator [7]. Inhibits binding of BclXL to Bak (IC50 = 1.5 microM) or Bad proteins and stimulates apoptosis in several cancer cell lines [10, 13]. Blocks human P2X7 receptor [11]. Induces cell cycle arrest in G1 phase [14]. Specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor [15]. - Chemical. CAS: 3895-92-9. Formula: C21H18ClNO4. MW: 383.8. Cell permeable potent inhibitor of protein kinase C. Does not inhibit tyrosine protein kinases, cAMP-dependent protein kinase or calcium/calmodulin-dependent protein kinase. Antiplatelet, anti-inflammatory, antibacterial and antitumor compound. Apoptosis inducer in cancer cells in vitro and in vivo. Activates MAPK and JUNK signaling pathways. Affects translocation of PKC from cytosol to plasma membrane. Neurite outgrowth stimulator. Inhibits binding of BclXL to Bak (IC50 = 1.5 microM) or Bad proteins and stimulates apoptosis in several cancer cell lines. Blocks human P2X7 receptor. Induces cell cycle arrest in G1 phase. Specific cyclooxygenase-2 inhibitor.
- SMILES[Cl-].COC1=C(OC)C2=C(C=C1)C1=C(C3=C(C=C1)C=C1OCOC1=C3)[N+](C)=C2
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200


![Chelerythrine chloride [3895-92-9]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/35/44/CgoaEWayGq6ETe5aAAAAAFiG2O4726.png)