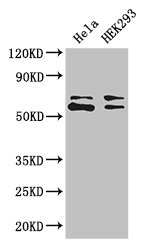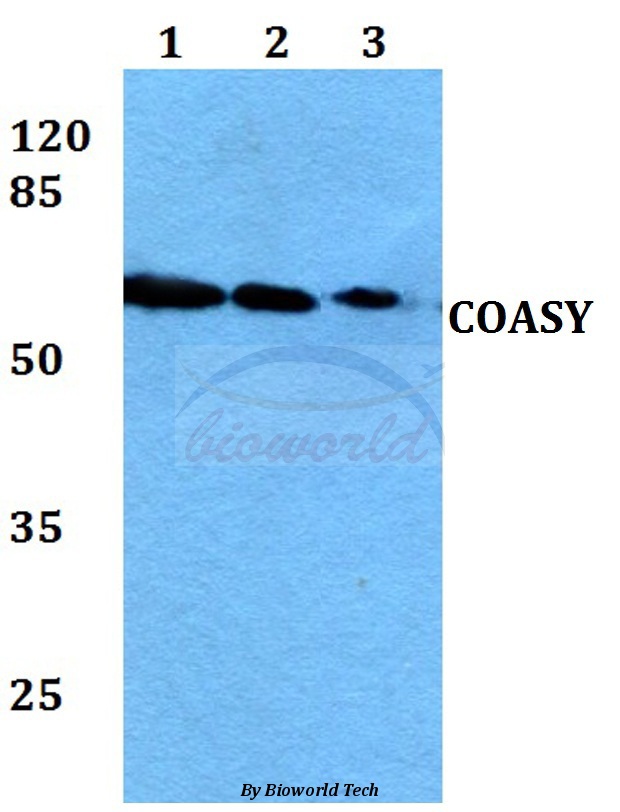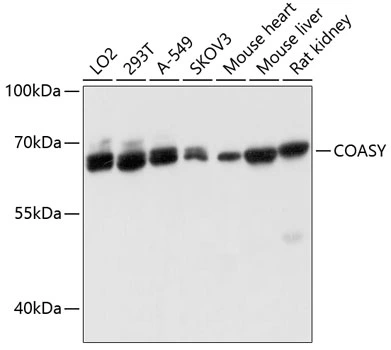
WB analysis of various sample lysates using GTX64695 COASY antibody. Dilution : 1:3000 Loading : 25μg per lane
COASY antibody
GTX64695
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetCOASY
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCOASY antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID80347
- Target nameCOASY
- Target descriptionCoenzyme A synthase
- Target synonymsDPCK, NBIA6, NBP, PCH12, PPAT, UKR1, pOV-2, bifunctional coenzyme A synthase, CoA synthase, bifunctional phosphopantetheine adenylyl transferase/dephospho CoA kinase, nucleotide binding protein, phosphopantetheine adenylyltransferase / dephosphocoenzyme A kinase
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ13057
- Protein NameBifunctional coenzyme A synthase
- Scientific DescriptionCoenzyme A (CoA) functions as a carrier of acetyl and acyl groups in cells and thus plays an important role in numerous synthetic and degradative metabolic pathways in all organisms. In eukaryotes, CoA and its derivatives are also involved in membrane trafficking and signal transduction. This gene encodes the bifunctional protein coenzyme A synthase (CoAsy) which carries out the last two steps in the biosynthesis of CoA from pantothenic acid (vitamin B5). The phosphopantetheine adenylyltransferase domain of this bifunctional protein catalyzes the conversion of 4-phosphopantetheine into dephospho-coenzyme A (dpCoA) while its dephospho-CoA kinase domain completes the final step by phosphorylating dpCoA to form CoA. Mutations in this gene are associated with neurodegeneration with brain iron accumulation (NBIA). Alternative splicing results in multiple isoforms. [provided by RefSeq, Apr 2014]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161