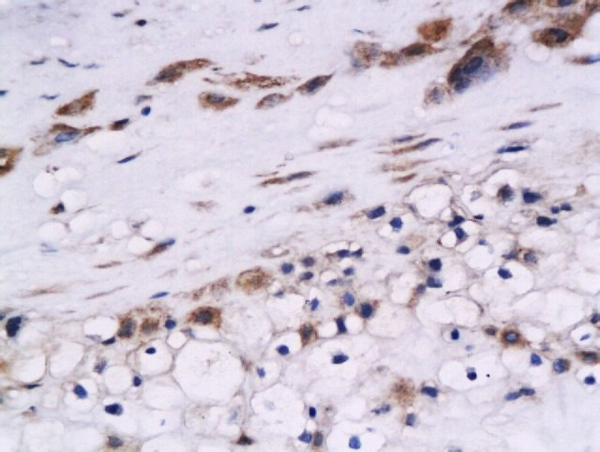
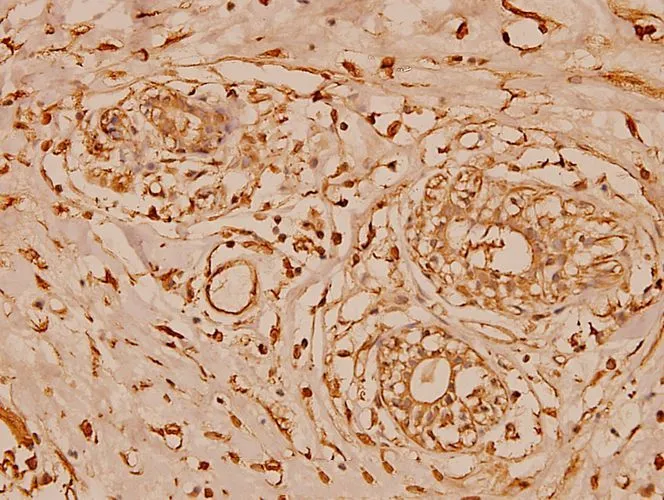
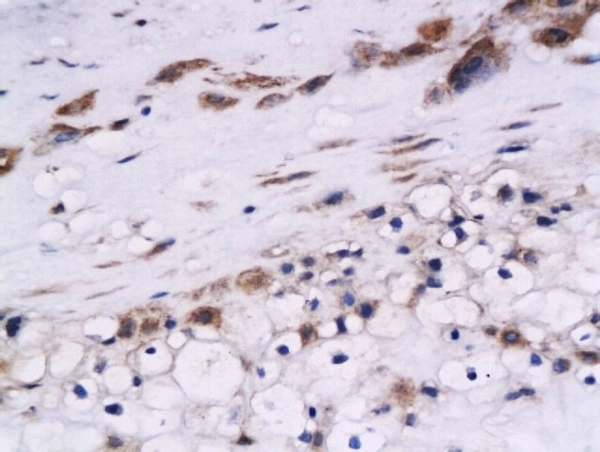
![WB analysis of A549 lysate (35ug) using Cystatin B antibody [2F1] at a dilution of 1:1,000. WB analysis of A549 lysate (35ug) using Cystatin B antibody [2F1] at a dilution of 1:1,000.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX53707/GTX53707_WB_w_23060900_557.webp)
WB analysis of A549 lysate (35ug) using Cystatin B antibody [2F1] at a dilution of 1:1,000.
Cystatin B antibody [2F1]
GTX53707
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetCSTB
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameCystatin B antibody [2F1]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteThe antibody has been tested by ELISA and Western blot analysis to assure specificity and reactivity. Since application varies, however, each investigation should be titrated by the reagent to obtain optimal results. Recommended dilution range for Western blot analysis is 1:1,000~ 2,000. Recommended starting dilution is 1:1,000.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID2F1
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1476
- Target nameCSTB
- Target descriptioncystatin B
- Target synonymsCPI-B, CST6, EPM1, EPM1A, PME, STFB, ULD, cystatin-B, cystatin B (stefin B), epididymis secretory sperm binding protein, liver thiol proteinase inhibitor
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2b
- Protein IDP04080
- Protein NameCystatin-B
- Scientific DescriptionThe cystatin superfamily encompasses proteins that contain multiple cystatin-like sequences. Some of the members are active cysteine protease inhibitors, while others have lost or perhaps never acquired this inhibitory activity. There are three inhibitory families in the superfamily, including the type 1 cystatins (stefins), type 2 cystatins and kininogens. This gene encodes a stefin that functions as an intracellular thiol protease inhibitor. The protein is able to form a dimer stabilized by noncovalent forces, inhibiting papain and cathepsins l, h and b. The protein is thought to play a role in protecting against the proteases leaking from lysosomes. Evidence indicates that mutations in this gene are responsible for the primary defects in patients with progressive myoclonic epilepsy (EPM1). One type of mutation responsible for EPM1 is the expansion in the promoter region of this gene of a CCCCGCCCCGCG repeat from 2-3 copies to 30-78 copies. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2016]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203