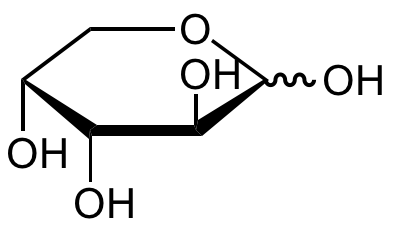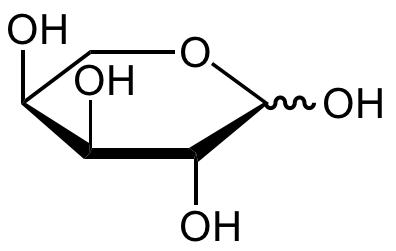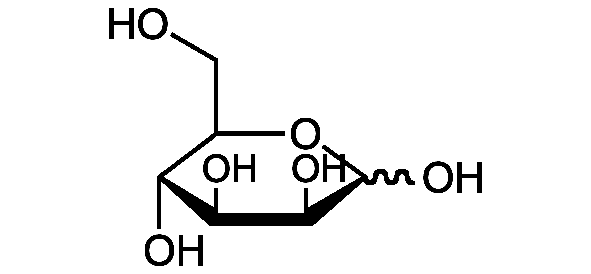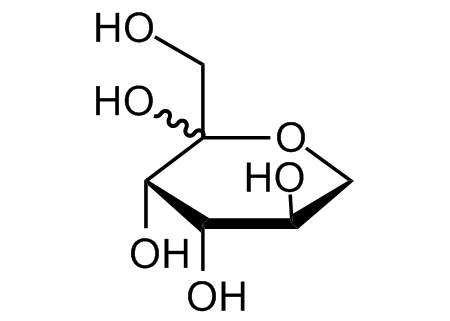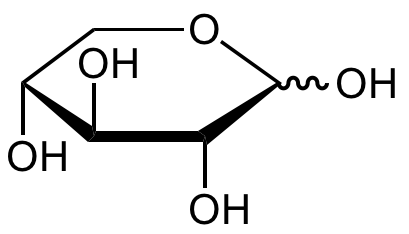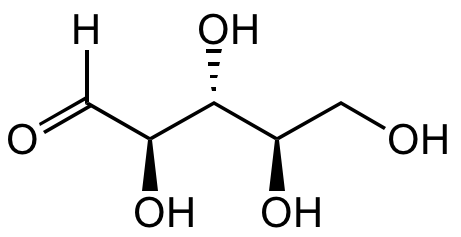
Chemical Structure
D-(-)-Ribose [50-69-1] [50-69-1]
CDX-R0065
CAS Number50-69-1
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight150.13
Overview
- SupplierChemodex
- Product NameD-(-)-Ribose [50-69-1] [50-69-1]
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CAS Number50-69-1
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC5H10O5
- Molecular Weight150.13
- Scientific DescriptionAldopentose monosaccharide that is phosphorylated into D-ribose 5-phosphate by ribokinase. D-ribose-5-phosphate supports the biosynthesis of the amino acids tryptophan and histidine, and is a component in the pentose phosphate pathway. D-ribose is present in all living cells and their microenvironments and is a key component of numerous biomolecules involved in many important metabolic pathways. It also participates in the glycation of proteins producing advanced glycation end products (AGEs) that lead to cell dysfunction and death. Ribosylation, has been shown to cause protein aggregation in vitro and in vivo. Has demonstrated significant enhancing abilities in replenishing deficient cellular energy levels following myocardial ischemia, improving depressed function in numerous animal investigations and showing cellular protection during oxidative stress. D-Ribose is used as a supplement in cell culture and as a building block for synthesis. - Chemical. CAS: 50-69-1. Formula: C5H10O5. MW: 150.13. Synthetic. Aldopentose monosaccharide that is phosphorylated into D-ribose 5-phosphate by ribokinase. D-ribose-5-phosphate supports the biosynthesis of the amino acids tryptophan and histidine, and is a component in the pentose phosphate pathway. D-ribose is present in all living cells and their microenvironments and is a key component of numerous biomolecules involved in many important metabolic pathways. It also participates in the glycation of proteins producing advanced glycation end products (AGEs) that lead to cell dysfunction and death. Ribosylation, has been shown to cause protein aggregation in vitro and in vivo. Has demonstrated significant enhancing abilities in replenishing deficient cellular energy levels following myocardial ischemia, improving depressed function in numerous animal investigations and showing cellular protection during oxidative stress. D-Ribose is used as a supplement in cell culture and as a building block for synthesis.
- SMILESO=C([H])[C@@H]([C@@H]([C@@H](CO)O)O)O
- Storage Instruction2°C to 8°C,RT
- UNSPSC12352200