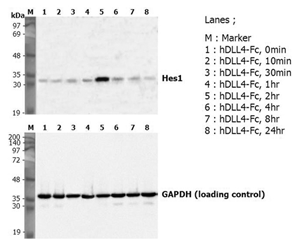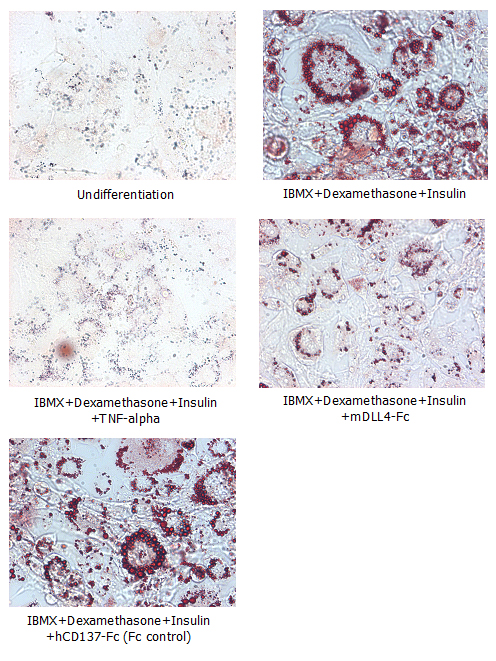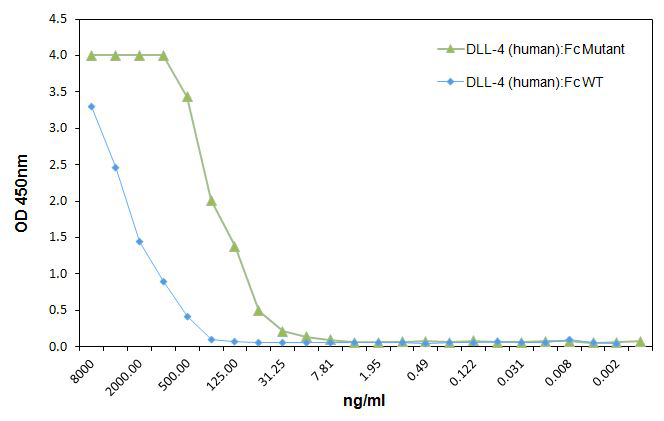
DLL4 (human):Fc (human) (rec.) (highly active mutant) (AG-40B-0176) binds to mNotch1 with higher affinity than WT DLL4:Fc. Method: Notch1 (mouse):Fc was coated on an ELISA plate at 1microg/ml. After blocking and washing steps, indicated concentrations
DLL4 (human):Fc (human) (rec.) (highly active mutant)
AG-40B-0176
Protein IDQ9NR61
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameDLL4 (human):Fc (human) (rec.) (highly active mutant)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID54567
- Target nameDLL4
- Target descriptiondelta like canonical Notch ligand 4
- Target synonymsAOS6, delta4, hdelta2, delta-like protein 4, delta 4, delta ligand 4, delta-like 4 homolog, delta-like 4 protein, drosophila Delta homolog 4, notch ligand DLL4, notch ligand delta-2
- Protein IDQ9NR61
- Protein NameDelta-like protein 4
- Scientific DescriptionProtein. Extracellular domain of human DLL4 (aa 27-529 plus mutations) are fused at the C-terminus to the Fc portion of human IgG1. Source: HEK 293 cells. Endotoxin content: 95% (SDS-PAGE). The Notch ligand delta-like protein 4 (DLL4) is expressed highly and selectively within the arterial endothelium and has been shown to function as a ligand for Notch1 and Notch4. It is induced by VEGF as a negative feedback regulator and acts to prevent overexuberant angiogenic sprouting, promoting the timely formation of a well differentiated vascular network. DLL4-Notch1 signaling regulates the formation of appropriate numbers of tip cells to control vessel sprouting and branching in the mouse retina. - The Notch ligand delta-like protein 4 (DLL4) is expressed highly and selectively within the arterial endothelium and has been shown to function as a ligand for Notch1 and Notch4. It is induced by VEGF as a negative feedback regulator and acts to prevent overexuberant angiogenic sprouting, promoting the timely formation of a well differentiated vascular network. DLL4-Notch1 signaling regulates the formation of appropriate numbers of tip cells to control vessel sprouting and branching in the mouse retina.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesHuman