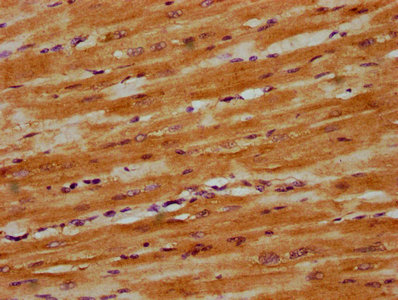
Immunohistochemistry of paraffin-embedded Human liver cancer tissue using DNAJC15 Polyclonal Antibody at dilution 1:40
DNAJC15 Polyclonal Antibody
E-AB-15068
Product group Antibodies
Overview
- SupplierElabscience
- Product NameDNAJC15 Polyclonal Antibody
- Delivery Days Customer12
- Applications SupplierELISA IHC
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration0.3mg/ml
- Scientific DescriptionThe DnaJ family is one of the largest of all the chaperone families and has evolved with diverse cellular localization and functions. The presence of a J domain defines a protein as a member of the DnaJ family. DnaJ heat shock induced proteins are from the bacterium Escherichia coli and are under the control of the htpR regulatory protein. The DnaJ proteins play a critical role in the HSP 70 chaperone machine by interacting with HSP 70 to stimulate ATP hydrolysis. DnaJ proteins are important mediators of proteolysis and are involved in the regulation of protein degradation, exocytosis and endocytosis. MCJ (methylation-controlled J protein), also known as HSD18, DNAJD1 or DNAJC15, is a 150 amino acid ubiquitously expressed single-pass membrane protein containing one J domain. Localizing to the golgi apparatus and only present in vertebrates, MCJ may be associated with increased chemotherapeutic resistance in ovarian cancer by inducing expression of the Mdr drug transporter and preventing intracellular drug accumulation.
- UNSPSC12352203