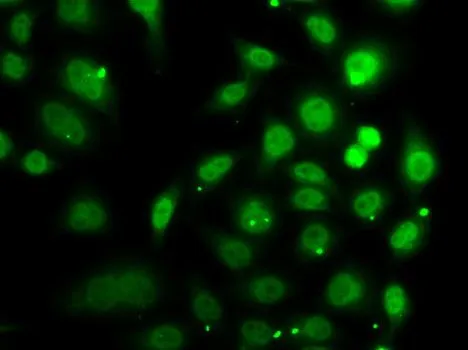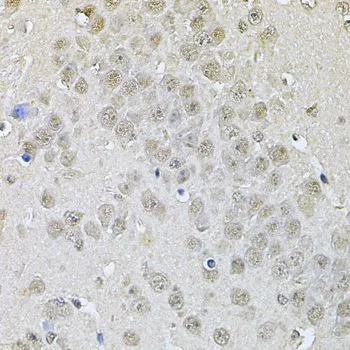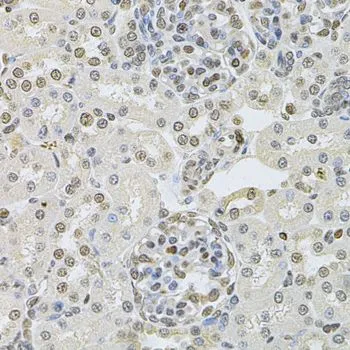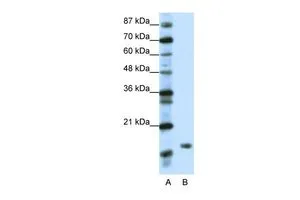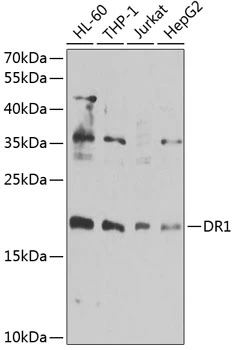
WB analysis of various sample lysates using GTX55597 DR1 antibody. Dilution : 1:1000 Loading : 25microg per lane
DR1 antibody
GTX55597
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetDR1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameDR1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. ICC/IF: 1:50 - 1:200. IHC-P: 1:50 - 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1810
- Target nameDR1
- Target descriptiondown-regulator of transcription 1
- Target synonymsNC2, NC2-BETA, NC2B, NCB2, protein Dr1, TATA-binding protein-associated phosphoprotein, negative cofactor 2, negative cofactor 2-beta
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ01658
- Protein NameProtein Dr1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a TBP- (TATA box-binding protein) associated phosphoprotein that represses both basal and activated levels of transcription. The encoded protein is phosphorylated in vivo and this phosphorylation affects its interaction with TBP. This protein contains a histone fold motif at the amino terminus, a TBP-binding domain, and a glutamine- and alanine-rich region. The binding of DR1 repressor complexes to TBP-promoter complexes may establish a mechanism in which an altered DNA conformation, together with the formation of higher order complexes, inhibits the assembly of the preinitiation complex and controls the rate of RNA polymerase II transcription. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Li H, Sun F, Bai S, et al. The DR1‑CSE/H(2)S system inhibits renal fibrosis by downregulating the ERK1/2 signaling pathway in diabetic mice. Int J Mol Med. 2022,49(1):pii: 7. doi: 10.3892/ijmm.2021.5062.Read this paper