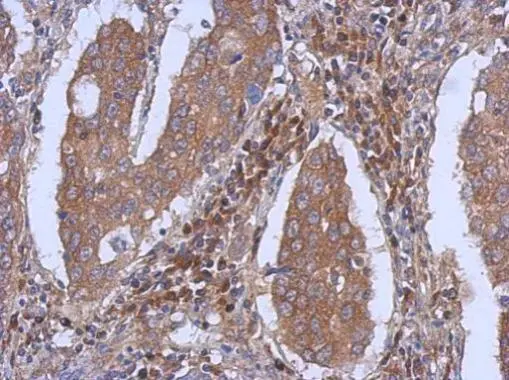
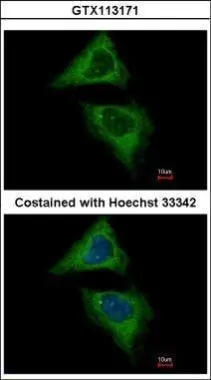
![Dynamin 2 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects DNM2 protein at cytoplasm by confocal immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: DNM2 protein stained by Dynamin 2 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX109652) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33343 staining. [Images captured by Olympus FV10i Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope] Dynamin 2 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects DNM2 protein at cytoplasm by confocal immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: DNM2 protein stained by Dynamin 2 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX109652) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33343 staining. [Images captured by Olympus FV10i Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope]](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX109652/GTX109652_40408_IFA_w_23060500_969.webp)
Dynamin 2 antibody [C2C3], C-term detects DNM2 protein at cytoplasm by confocal immunofluorescent analysis. Sample: HeLa cells were fixed in ice-cold MeOH for 5 min. Green: DNM2 protein stained by Dynamin 2 antibody [C2C3], C-term (GTX109652) diluted at 1:500. Blue: Hoechst 33343 staining. [Images captured by Olympus FV10i Confocal Laser Scanning Microscope]
Dynamin 2 antibody [C2C3], C-term
GTX109652
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetDNM2
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameDynamin 2 antibody [C2C3], C-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500-1:3000. ICC/IF: 1:100-1:1000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.44 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1785
- Target nameDNM2
- Target descriptiondynamin 2
- Target synonymsCMT2M, CMTDI1, CMTDIB, DI-CMTB, DYN2, DYNII, LCCS5, dynamin-2, dynamin II
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP50570
- Protein NameDynamin-2
- Scientific DescriptionDynamins represent one of the subfamilies of GTP-binding proteins. These proteins share considerable sequence similarity over the N-terminal portion of the molecule, which contains the GTPase domain. Dynamins are associated with microtubules. They have been implicated in cell processes such as endocytosis and cell motility, and in alterations of the membrane that accompany certain activities such as bone resorption by osteoclasts. Dynamins bind many proteins that bind actin and other cytoskeletal proteins. Dynamins can also self-assemble, a process that stimulates GTPase activity. Four alternatively spliced transcripts encoding different proteins have been described. Additional alternatively spliced transcripts may exist, but their full-length nature has not been determined. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161