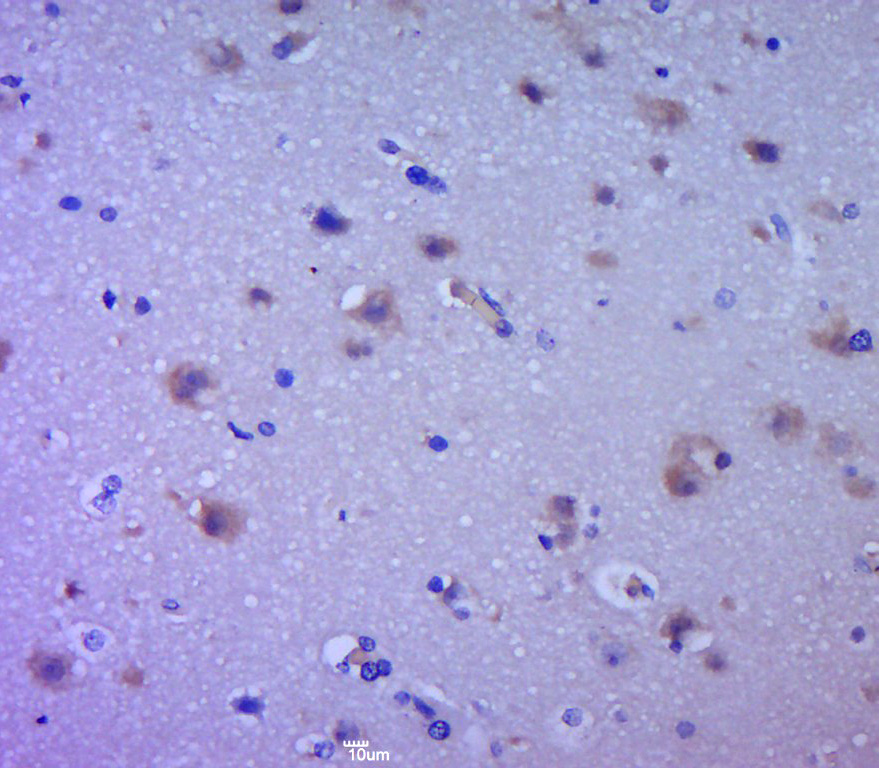
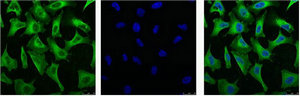
EGFR antibody [29.1]
GTX10414
ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityCanine, Human, Mouse, Porcine, Rat
TargetEGFR
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameEGFR antibody [29.1]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:3,000. ELISA: 1:10,000. IHC: 1:50. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ELISA, ImmunoHistoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID29.1
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1956
- Target nameEGFR
- Target descriptionepidermal growth factor receptor
- Target synonymsERBB, ERBB1, ERRP, HER1, NISBD2, NNCIS, PIG61, mENA, epidermal growth factor receptor, EGFR vIII, avian erythroblastic leukemia viral (v-erb-b) oncogene homolog, cell growth inhibiting protein 40, cell proliferation-inducing protein 61, epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase domain, erb-b2 receptor tyrosine kinase 1, proto-oncogene c-ErbB-1, receptor tyrosine-protein kinase erbB-1
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG1
- Protein IDP00533
- Protein NameEpidermal growth factor receptor
- Scientific DescriptionThe receptor for Epidermal Growth Factor is an integral cell membrane protein of 170 kDa, which spans the membranes of a wide range of normal and malignant epithelial cells. It is a tyrosine-specific protein kinase with the capacity to phosphorylate tyrosine residues located near its carboxy-terminus. EGF-R has anextracellular region which binds EGF and consequently mediates the initial response of cells to EGF and an intra- cellular region which posseses the tyrosine kinase activity. As a result of EGF binding to its specific receptor, there is increased DNA synthesis as well as other events such as cell proliferation, differentiationand repair of damaged epithelial tissue. The EGF-R has a half-life of approximately 10 hours in human fibroblasts, but in the presence of EGF this value is reduced to about 1 hour. A close similarity has been found between the sequence of the v-erb-B oncogene and the cytoplasmic and transmembrane part of the EGF-R (truncated EGF-R). It is hypothesized that an inappropriate activation of the human erb-B gene either by truncation or overexpression plays a role in the development of the malignancy. This hypothesis is supported by studies which have shown an increased number of EGF-R in various malignant tumors. High levels of EGF-R have been identified in sarcomas, gliomas, gynecological, breast, bladder and lungtumors.
- ReactivityCanine, Human, Mouse, Porcine, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161