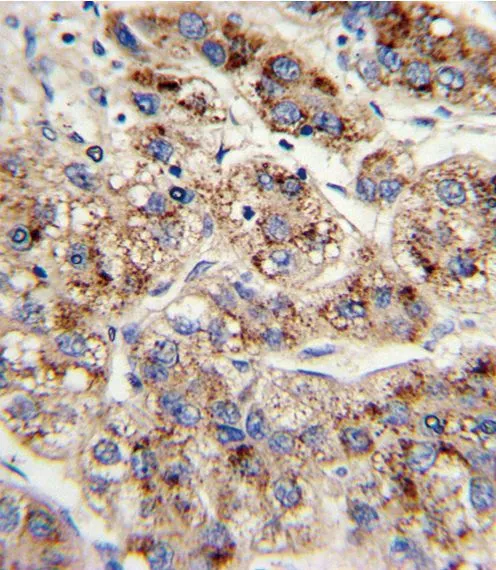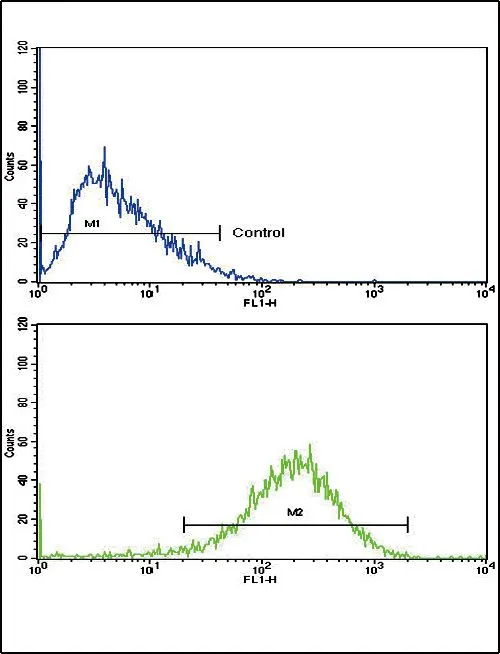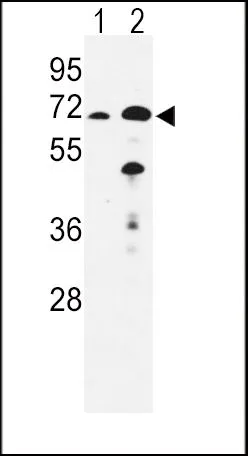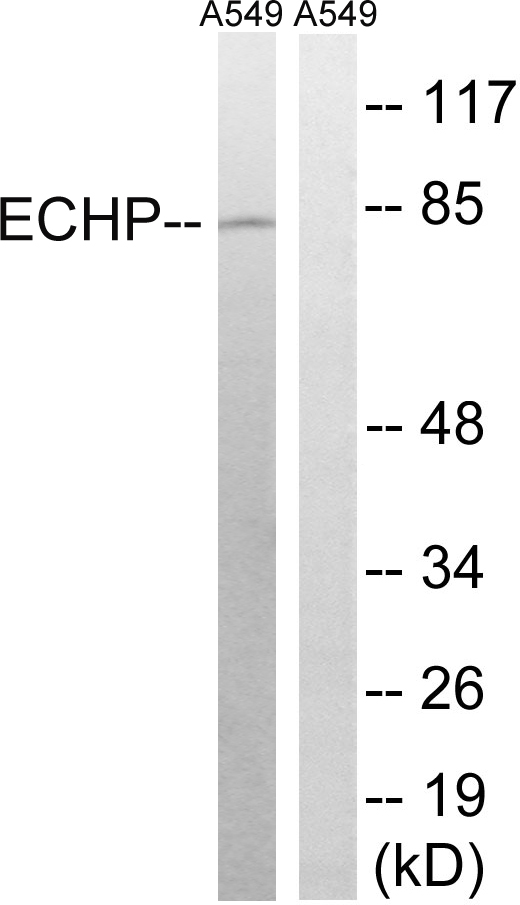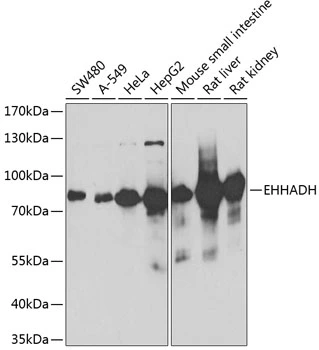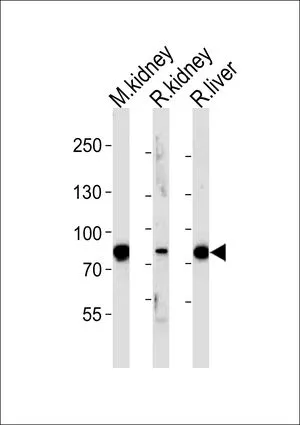
WB analysis of mouse kidney, rat kidney and liver tissue using GTX81126 EHHADH antibody, C-term. Loading : 35ug per lane Dilution : 1:1000
EHHADH antibody, C-term
GTX81126
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetEHHADH
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameEHHADH antibody, C-term
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000. IHC-P: 1:10-1:50. FCM: 1:10-1:50. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID1962
- Target nameEHHADH
- Target descriptionenoyl-CoA hydratase and 3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase
- Target synonymsECHD, FRTS3, L-PBE, LBFP, LBP, MFE1, PBFE, peroxisomal bifunctional enzyme, 3,2-trans-enoyl-CoA isomerase, L-3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase, L-bifunctional protein, peroxisomal, PBE, enoyl-CoA, hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl CoA dehydrogenase, enoyl-Coenzyme A, hydratase/3-hydroxyacyl Coenzyme A dehydrogenase, multifunctional enzyme 1, peroxisomal enoyl-CoA hydratase
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ08426
- Protein NamePeroxisomal bifunctional enzyme
- Scientific DescriptionThe protein encoded by this gene is a bifunctional enzyme and is one of the four enzymes of the peroxisomal beta-oxidation pathway. The N-terminal region of the encoded protein contains enoyl-CoA hydratase activity while the C-terminal region contains 3-hydroxyacyl-CoA dehydrogenase activity. Defects in this gene are a cause of peroxisomal disorders such as Zellweger syndrome. Two transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been found for this gene. [provided by RefSeq, Oct 2009]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161
References
- Peroxisomal L-bifunctional protein (EHHADH) deficiency causes male-specific kidney hypertrophy and proximal tubular injury in mice. Ranea-Robles P et al., 2021 Sep, Kidney360Read this paper
- The peroxisomal transporter ABCD3 plays a major role in hepatic dicarboxylic fatty acid metabolism and lipid homeostasis. Ranea-Robles P et al., 2021 Nov, J Inherit Metab DisRead this paper
- Murine deficiency of peroxisomal L-bifunctional protein (EHHADH) causes medium-chain 3-hydroxydicarboxylic aciduria and perturbs hepatic cholesterol homeostasis. Ranea-Robles P et al., 2021 Jul, Cell Mol Life SciRead this paper
- Peroxisomes can oxidize medium- and long-chain fatty acids through a pathway involving ABCD3 and HSD17B4. Violante S et al., 2019 Mar, FASEB JRead this paper