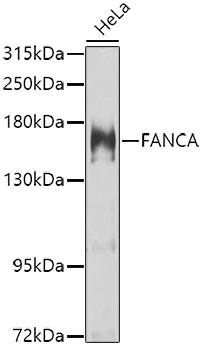
WB analysis of HeLa cell lysate using GTX55613 FANCA antibody. Dilution : 1:1000 Loading : 25μg per lane
FANCA antibody
GTX55613
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetFANCA
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameFANCA antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:500 - 1:2000. IHC-P: 1:50 - 1:200. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID2175
- Target nameFANCA
- Target descriptionFA complementation group A
- Target synonymsFA, FA-H, FA1, FAA, FACA, FAH, FANCH, Fanconi anemia group A protein, Fanconi anemia complementation group A, Fanconi anemia, complementation group H, Fanconi anemia, type 1
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDO15360
- Protein NameFanconi anemia group A protein
- Scientific DescriptionThe Fanconi anemia complementation group (FANC) currently includes FANCA, FANCB, FANCC, FANCD1 (also called BRCA2), FANCD2, FANCE, FANCF, FANCG, FANCI, FANCJ (also called BRIP1), FANCL, FANCM and FANCN (also called PALB2). The previously defined group FANCH is the same as FANCA. Fanconi anemia is a genetically heterogeneous recessive disorder characterized by cytogenetic instability, hypersensitivity to DNA crosslinking agents, increased chromosomal breakage, and defective DNA repair. The members of the Fanconi anemia complementation group do not share sequence similarity; they are related by their assembly into a common nuclear protein complex. This gene encodes the protein for complementation group A. Alternative splicing results in multiple transcript variants encoding different isoforms. Mutations in this gene are the most common cause of Fanconi anemia. [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2008]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161





![Western blot using GeneTex's affinity purified anti-FANCA antibody shows detection of a band at ~133 kDa (arrowhead) corres-ponding to FANCA in HeLa whole cell lysates. The identity of the lower molecular weight bands is unknown but may represent breakdown products. Approximately 35 ug of lysate was separated by 4-20% Tris Glycine SDS-PAGE. After blocking, the membrane was probed for 2 h at room temperature with the primary antibody diluted to 1:1,500. The membrane was washed and reacted with a 1:10,000 dilution of IRDye?800 conjugated Gt-a-Rabbit IgG [H&L] for 45 min at room temperature (800 nm channel, green). Molecular weight estimation was made by comparison to prestained MW markers indicated at left (700 nm channel, red). IRDye?800 fluorescence images were captured using the OdysseyR Infrared Imaging System developed by LI-COR. IRDye is a trademark of LI-COR, Inc. Other detection systems will yield similar results.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX25063/GTX25063_20160330_WB_w_23060722_398.webp)