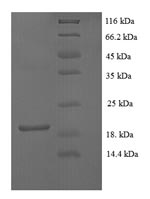
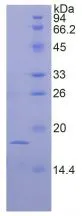
FGF-1 (mouse) (rec.) (untagged)
AG-40B-0148
Protein IDP61148
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameFGF-1 (mouse) (rec.) (untagged)
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Concentration0.1 mg/ml
- Estimated Purity>95%
- Gene ID14164
- Target nameFgf1
- Target descriptionfibroblast growth factor 1
- Target synonymsDffrx, Fam, Fgf-1, Fgf2b, Fgfa, fibroblast growth factor 1, HBGF-1, aFGF, acidic fibroblast growth factor, fibroblast growth factor 1 (acidic), fibroblast growth factor 2b, heparin-binding growth factor 1
- Protein IDP61148
- Protein NameFibroblast growth factor 1
- Scientific DescriptionFibroblast growth factors (FGFs) constitute a family of heparin-binding polypeptides involved in the regulation of biological responses such as growth, differentiation and angiogenesis. The biological effects of FGFs are mediated by four structurally related receptor tyrosine kinases denoted FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. FGF-1 [FGF-acidic; ECGF; HBGF-1] is a powerful mitogen of cells of mesodermal, ectodermal and endodermal origin. FGF-1 association with heparan sulfate is a prerequisite for activation of FGF receptors. FGF-1 plays a role in various stages of development and morphogenesis as well as in angiogenesis and wound healing processes. Recent data indicate a role of FGF-1 in inflammation and obesity. FGF-1 is selectively induced in fat cells by high-fat diet feeding and established the PPARgamma-FGF-1 axis as a critical pathway that regulates adipose tissue remodeling. - Protein. Mouse FGF-1 (aa 16-155) is untagged. Source: E. coli. Endotoxin content: 95% (SDS-PAGE). Fibroblast growth factors (FGFs) constitute a family of heparin-binding polypeptides involved in the regulation of biological responses such as growth, differentiation and angiogenesis. The biological effects of FGFs are mediated by four structurally related receptor tyrosine kinases denoted FGFR1, FGFR2, FGFR3 and FGFR4. FGF-1 is a powerful mitogen of cells of mesodermal, ectodermal and endodermal origin. FGF-1 association with heparan sulfate is a prerequisite for activation of FGF receptors. FGF-1 plays a role in various stages of development and morphogenesis as well as in angiogenesis and wound healing processes. Recent data indicate a role of FGF-1 in inflammation and obesity. FGF-1 is selectively induced in fat cells by high-fat diet feeding and established the PPARgamma-FGF-1 axis as a critical pathway that regulates adipose tissue remodeling.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116100
- SpeciesMouse