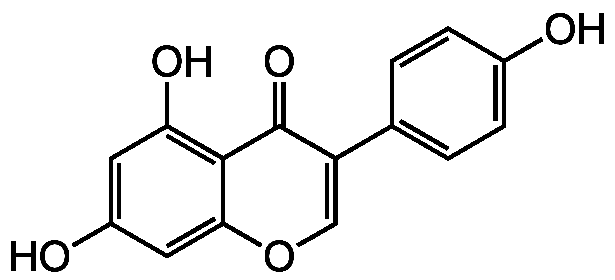
Chemical Structure
Genistein [446-72-0]
AG-CN2-0427
CAS Number446-72-0
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>99%
Molecular Weight270.2
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameGenistein [446-72-0]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number446-72-0
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>99%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC15H10O5
- Molecular Weight270.2
- Scientific DescriptionCell-permeable, reversible, substrate competitive tyrosine kinase inhibitor (including EGFR phosphorylation), implicated in almost all cell growth and proliferation signal cascades [1]. Inhibitor of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II [2]. Anticancer agent, inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis [3]. Antiangiogenic agent, down-regulates the transcription of genes involved in controlling angiogenesis [12]. Binds estrogen receptor beta. Can increase the rate of growth of some ER expressing breast cancers [4, 10]. Potent alpha-glucosidase inhibitor [5]. Anthelmintic [6]. Anti-diabetic. Activates nuclear receptors, oestrogen receptors and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (all PPAR isoforms) and it inhibits various enzyme activities [7, 8, 14]. Inhibitor of GLUT4-mediated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes [9]. Stimulator of autophagy vacuolization [12]. Antioxidant [13]. TRAIL sensitizer [15]. Acts as an agonist at the GPR30 receptor [16]. MALT1 inhibitor [17] DNA methyltransferase inhibitor [18]. Genistein exhibits synergistic antibacterial effects on MRSA [19]. - Chemical. CAS: 446-72-0. Formula: C15H10O5. MW: 270.2. Synthetic. Cell-permeable, reversible, substrate competitive tyrosine kinase inhibitor (including EGFR phosphorylation), implicated in almost all cell growth and proliferation signal cascades. Inhibitor of mammalian DNA topoisomerase II. Anticancer agent, inducing cell cycle arrest and apoptosis. Antiangiogenic agent, down-regulates the transcription of genes involved in controlling angiogenesis. Binds estrogen receptor beta. Can increase the rate of growth of some ER expressing breast cancers. Potent alpha-glucosidase inhibitor. Anthelmintic. Anti-diabetic. Activates nuclear receptors, oestrogen receptors and peroxisome proliferator-activated receptors (all PPAR isoforms) and it inhibits various enzyme activities. Inhibitor of GLUT4-mediated glucose uptake in 3T3-L1 adipocytes. Stimulator of autophagy vacuolization. Antioxidant. TRAIL sensitizer. Acts as an agonist at the GPR30 receptor. MALT1 inhibitor DNA methyltransferase inhibitor. Genistein exhibits synergistic antibacterial effects on MRSA.
- SMILESOC1=CC=C(C=C1)C1=COC2=CC(O)=CC(O)=C2C1=O
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

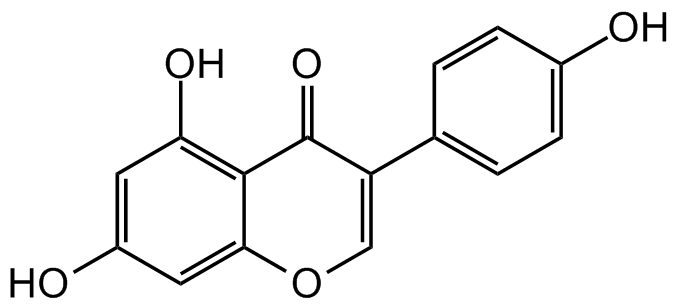

![Genistein [446-72-0]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/2A/03/CgoaEGaCtfiELpetAAAAAHPXo4Q042.png)