HDAC4 antibody [HDAC-144]
GTX12171
ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
TargetHDAC4
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHDAC4 antibody [HDAC-144]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1-2 microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsImmunoFluorescence, ImmunoPrecipitation, Western Blot, ImmunoCytoChemistry
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDHDAC-144
- Concentration2 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID9759
- Target nameHDAC4
- Target descriptionhistone deacetylase 4
- Target synonymsAHO3, BDMR, HA6116, HD4, HDAC-4, HDAC-A, HDACA, NEDCHF, NEDCHID, histone deacetylase 4, histone deacetylase A
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Protein IDP56524
- Protein NameHistone deacetylase 4
- Scientific DescriptionChromatin is a highly specialized structure composed of tightly compacted chromosomal DNA. Gene expression within the nucleus is controlled, in part, by a host of protein complexes which continuously pack and unpack the chromosomal DNA. One of the known mechanisms of this packing and unpacking process involves the acetylation and deacetylation of the histone proteins comprising the nucleosomal core. Acetylated histone proteins confer accessibility of the DNA template to the transcriptional machinery for expression. Histone deacetylases (HDACs) are chromatin remodeling factors that deacetylate histone proteins and thus, may act as transcriptional repressors. HDACs are classified by their sequence homology to the yeast HDACs and there are currently 2 classes. Class I proteins are related to Rpd3 and members of class II resemble Hda1p.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse, Rat
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Sluijter JP, van Mil A, van Vliet P, et al. MicroRNA-1 and -499 regulate differentiation and proliferation in human-derived cardiomyocyte progenitor cells. Arterioscler Thromb Vasc Biol. 2010,30(4):859-68. doi: 10.1161/ATVBAHA.109.197434Read this paper


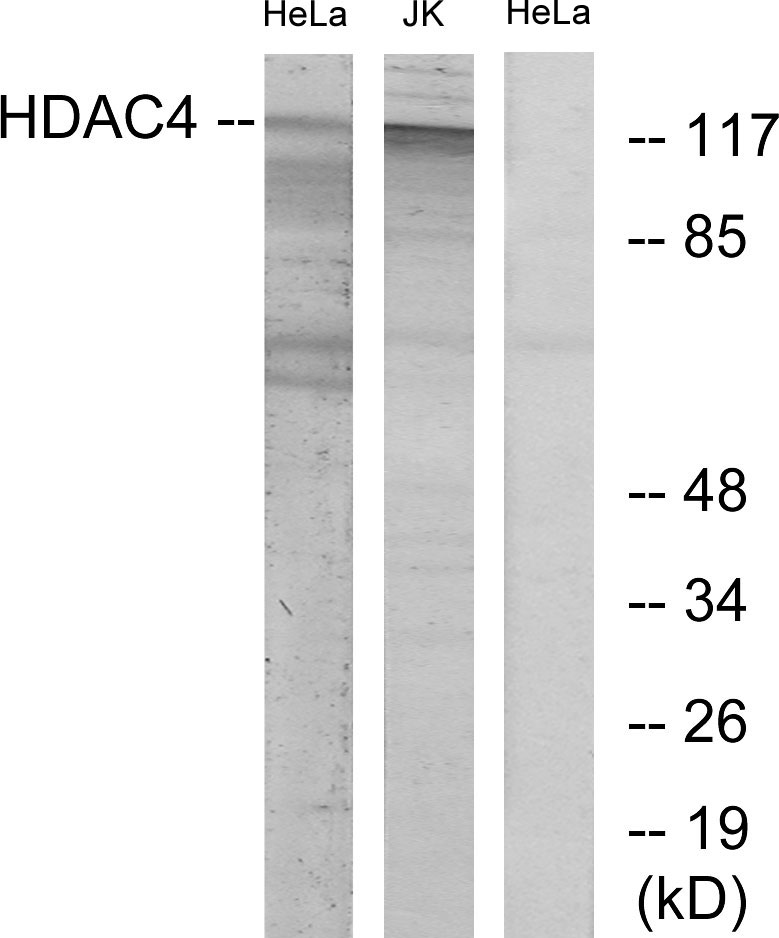

![WB analysis of HeLa (1), Jurkat (2) cell lysate using GTX83229 HDAC4 antibody [7B2].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX83229/GTX83229_20170912_WB_w_23061322_126.webp)