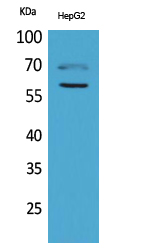
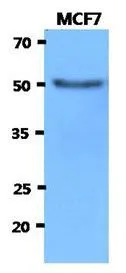
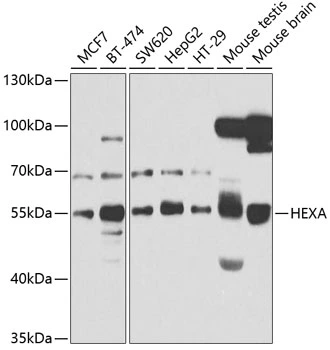
![WB analysis of L1210 (1), and HL7702 (2) cell lysate using GTX60574 HEXA antibody [3F10]. WB analysis of L1210 (1), and HL7702 (2) cell lysate using GTX60574 HEXA antibody [3F10].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60574/GTX60574_20170912_WB_w_23061123_267.webp)
WB analysis of L1210 (1), and HL7702 (2) cell lysate using GTX60574 HEXA antibody [3F10].
HEXA antibody [3F10]
GTX60574
ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ELISA
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetHEXA
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameHEXA antibody [3F10]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1/500 - 1/2000. FCM: 1/200 - 1/400. ELISA: 1/10000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsFlow Cytometry, Western Blot, ELISA
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone ID3F10
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3073
- Target nameHEXA
- Target descriptionhexosaminidase subunit alpha
- Target synonymsTSD, beta-hexosaminidase subunit alpha, N-acetyl-beta-glucosaminidase subunit alpha, beta-N-acetylhexosaminidase subunit alpha, hexosaminidase A (alpha polypeptide), hexosaminidase subunit A
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2b
- Protein IDP06865
- Protein NameBeta-hexosaminidase subunit alpha
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes the alpha subunit of the lysosomal enzyme beta-hexosaminidase that, together with the cofactor GM2 activator protein, catalyzes the degradation of the ganglioside GM2, and other molecules containing terminal N-acetyl hexosamines. Beta-hexosaminidase is composed of two subunits, alpha and beta, which are encoded by separate genes. Both beta-hexosaminidase alpha and beta subunits are members of family 20 of glycosyl hydrolases. Mutations in the alpha or beta subunit genes lead to an accumulation of GM2 ganglioside in neurons and neurodegenerative disorders termed the GM2 gangliosidoses. Alpha subunit gene mutations lead to Tay-Sachs disease (GM2-gangliosidosis type I). [provided by RefSeq, Jul 2009]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

![ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60574 HEXA antibody [3F10].
Black : Control antigen 100ng
Purple : Antigen 10ng
Blue : Antigen 50ng
Red : Antigen 100ng ELISA analysis of antigen using GTX60574 HEXA antibody [3F10].
Black : Control antigen 100ng
Purple : Antigen 10ng
Blue : Antigen 50ng
Red : Antigen 100ng](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60574/GTX60574_20170912_ELISA_w_23061123_701.webp)
![FACS analysis of HeLa cells using GTX60574 HEXA antibody [3F10]. Green : HEXA Red : negative control FACS analysis of HeLa cells using GTX60574 HEXA antibody [3F10]. Green : HEXA Red : negative control](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX60574/GTX60574_20170912_FACS_w_23061123_786.webp)