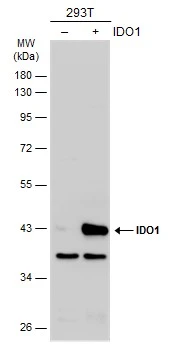
![Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membranes were blotted with IDO1 antibody [GT273] (GTX634652) diluted at 1:5000 and competitor's antibody (CST#12006) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. *The competitor is not affiliated with GeneTex and does not endorse this product. Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membranes were blotted with IDO1 antibody [GT273] (GTX634652) diluted at 1:5000 and competitor's antibody (CST#12006) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. *The competitor is not affiliated with GeneTex and does not endorse this product.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634652/GTX634652_43234_20181026_WB_B_competitor_watermark_w_23061202_260.webp)
Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membranes were blotted with IDO1 antibody [GT273] (GTX634652) diluted at 1:5000 and competitor's antibody (CST#12006) diluted at 1:1000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. *The competitor is not affiliated with GeneTex and does not endorse this product.
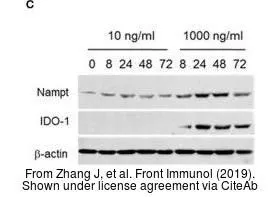
IDO1 antibody [GT273]
GTX634652
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetIDO1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameIDO1 antibody [GT273]
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000-1:10000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityMonoclonal
- Clone IDGT273
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID3620
- Target nameIDO1
- Target descriptionindoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1
- Target synonymsIDO, IDO-1, INDO, indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1, indolamine 2,3 dioxygenase, indole 2,3-dioxygenase, indoleamine-pyrrole 2,3-dioxygenase
- HostMouse
- IsotypeIgG2a
- Protein IDP14902
- Protein NameIndoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase 1
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes indoleamine 2,3-dioxygenase (IDO) - a heme enzyme that catalyzes the first and rate-limiting step in tryptophan catabolism to N-formyl-kynurenine. This enzyme acts on multiple tryptophan substrates including D-tryptophan, L-tryptophan, 5-hydroxy-tryptophan, tryptamine, and serotonin. This enzyme is thought to play a role in a variety of pathophysiological processes such as antimicrobial and antitumor defense, neuropathology, immunoregulation, and antioxidant activity. Through its expression in dendritic cells, monocytes, and macrophages this enzyme modulates T-cell behavior by its peri-cellular catabolization of the essential amino acid tryptophan.[provided by RefSeq, Feb 2011]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203
References
- Xu C, Feng C, Huang P, et al. TNFα and IFNγ rapidly activate PI3K-AKT signaling to drive glycolysis that confers mesenchymal stem cells enhanced anti-inflammatory property. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2022,13(1):491. doi: 10.1186/s13287-022-03178-3Read this paper
- Sorrentino C, D'Antonio L, Fieni C, et al. Colorectal Cancer-Associated Immune Exhaustion Involves T and B Lymphocytes and Conventional NK Cells and Correlates With a Shorter Overall Survival. Front Immunol. 2021,12:778329. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2021.778329Read this paper

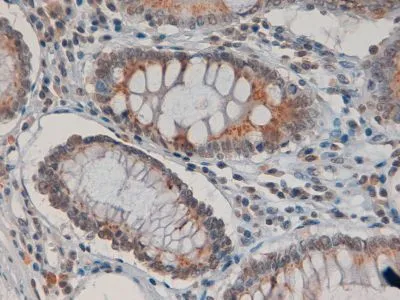
![IDO1 antibody [GT273] detects IDO1 protein at cell membrane and cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human tonsil. IDO1 stained by IDO1 antibody [GT273] (GTX634652) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min IDO1 antibody [GT273] detects IDO1 protein at cell membrane and cytoplasm by immunohistochemical analysis. Sample: Paraffin-embedded human tonsil. IDO1 stained by IDO1 antibody [GT273] (GTX634652) diluted at 1:200. Antigen Retrieval: Citrate buffer, pH 6.0, 15 min](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634652/GTX634652_44524_20220121_IHC-P_w_23061202_761.webp)
![Untreated (–) and treated (+) A549 whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with IDO1 antibody [GT273] (GTX634652) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody. Untreated (–) and treated (+) A549 whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 10% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with IDO1 antibody [GT273] (GTX634652) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-mouse IgG antibody (GTX213111-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX634652/GTX634652_44524_20211210_WB_treatment_IFN-gamma_w_23061202_391.webp)