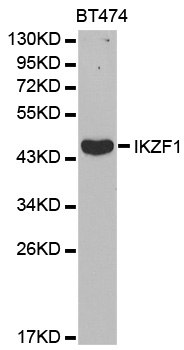
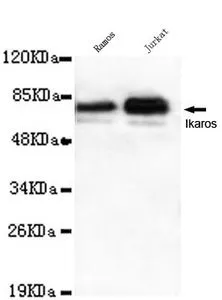
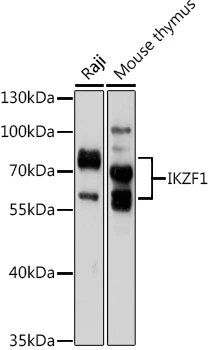
WB analysis of Molt-4 cell lysate using GTX88621 Ikaros antibody, Internal. Dilution : 0.03μg/ml Loading : 35μg protein in RIPA buffer
Ikaros antibody, Internal
GTX88621
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman
TargetIKZF1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameIkaros antibody, Internal
- Delivery Days Customer7
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 0.01-0.03microg/ml. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.50 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID10320
- Target nameIKZF1
- Target descriptionIKAROS family zinc finger 1
- Target synonymsCVID13, Hs.54452, IK1, IKAROS, LYF1, LyF-1, PPP1R92, PRO0758, ZNFN1A1, DNA-binding protein Ikaros, CLL-associated antigen KW-6, ikaros family zinc finger protein 1, lymphoid transcription factor LyF-1, protein phosphatase 1, regulatory subunit 92, zinc finger protein, subfamily 1A, 1 (Ikaros)
- HostGoat
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDQ13422
- Protein NameDNA-binding protein Ikaros
- Scientific DescriptionThis gene encodes a transcription factor that belongs to the family of zinc-finger DNA-binding proteins associated with chromatin remodeling. The expression of this protein is restricted to the fetal and adult hemo-lymphopoietic system, and it functions as a regulator of lymphocyte differentiation. Several alternatively spliced transcript variants encoding different isoforms have been described for this gene. Most isoforms share a common C-terminal domain, which contains two zinc finger motifs that are required for hetero- or homo-dimerization, and for interactions with other proteins. The isoforms, however, differ in the number of N-terminal zinc finger motifs that bind DNA and in nuclear localization signal presence, resulting in members with and without DNA-binding properties. Only a few isoforms contain the requisite three or more N-terminal zinc motifs that confer high affinity binding to a specific core DNA sequence element in the promoters of target genes. The non-DNA-binding isoforms are largely found in the cytoplasm, and are thought to function as dominant-negative factors. Overexpression of some dominant-negative isoforms have been associated with B-cell malignancies, such as acute lymphoblastic leukemia (ALL). [provided by RefSeq, May 2014]
- ReactivityHuman
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352203

![IHC-P analysis of mouse spleen tissue section using GTX01051 Ikaros antibody [JB50-38].](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX01051/GTX01051_20200303_IHC-P_328_w_23053121_974.webp)