IL-2 (C145S Mutant) (human) (rec.) (His)
CHI-HF-20102
Product group Proteins / Signaling Molecules
Overview
- SupplierChimerigen Laboratories
- Product NameIL-2 (C145S Mutant) (human) (rec.) (His)
- Delivery Days Customer2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>95%
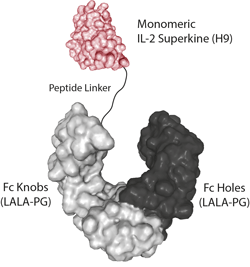
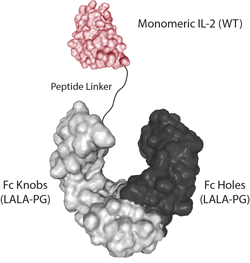
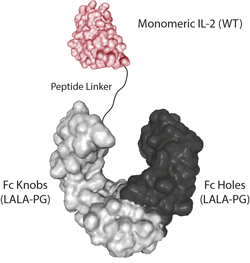
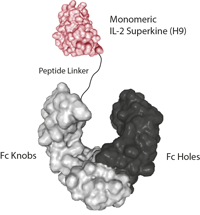
- Scientific DescriptionInterleukin-2 (IL-2) is a 133 amino acid glycoprotein with one intramolecular disulfide bond and variable glycosylation. It is secreted by activated T cells and induces proliferation and maturation of activated T cells, natural killer cells, and lymphokine activated killer cells. IL-2 also stimulates proliferation of antibody-producing B cells, activates neutrophils, and induces mononuclear cells to secrete IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha and -beta. Moreover, studies have shown that IL-2 is required for activation-induced apoptosis, an important hemeostatic mechanism in the immune system, which is involved in the maintenance of peripheral tolerance to self-antigens. The modified IL-2 protein containing a substitution at position C145S retains full biological activity, suggesting that the cysteine at this position is not involved in a disulfide bond and that a free sulfhydryl group at that position is not necessary for receptor binding. Additionally, the C145S mutation insertion avoids non-specific disulfides and improves the physical properties of the protein. - Protein. Human IL-2 (aa 21-153) (mutation C145S) is fused at the C-terminus to a His-tag. Source: HEK 293 cells. Endotoxin content: 95% (SDS-PAGE). Interleukin-2 (IL-2) is a 133 amino acid glycoprotein with one intramolecular disulfide bond and variable glycosylation. It is secreted by activated T cells and induces proliferation and maturation of activated T cells, natural killer cells, and lymphokine activated killer cells. IL-2 also stimulates proliferation of antibody-producing B cells, activates neutrophils, and induces mononuclear cells to secrete IFN-gamma and TNF-alpha and -beta. Moreover, studies have shown that IL-2 is required for activation-induced apoptosis, an important hemeostatic mechanism in the immune system, which is involved in the maintenance of peripheral tolerance to self-antigens. The modified IL-2 protein containing a substitution at position C145S retains full biological activity, suggesting that the cysteine at this position is not involved in a disulfide bond and that a free sulfhydryl group at that position is not necessary for receptor binding. Additionally, the C145S mutation insertion avoids non-specific disulfides and improves the physical properties of the protein.
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116120
- SpeciesHuman, Mouse

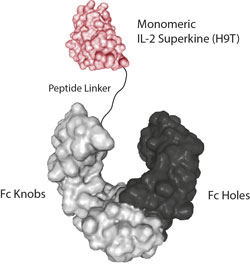
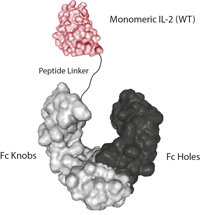
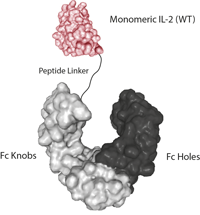
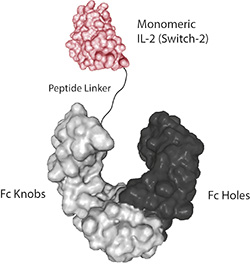
![IL-2 Superkine (Fc) [IL-2 (human):Fc (human) (rec.)]](https://adipogen.com/pub/media/catalog/product/a/g/ag-40b-0111-superkine_elisa-new.jpg)