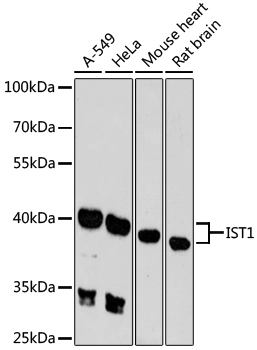
IST1 antibody
GTX101972
ApplicationsWestern Blot
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetIST1
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameIST1 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- ApplicationsWestern Blot
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration1 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID9798
- Target nameIST1
- Target descriptionIST1 factor associated with ESCRT-III
- Target synonymsCHMP8, OLC1, IST1 homolog, IST1, ESCRT-III associated factor, IST1, endosomal sorting complex required for transport-III component, charged multivesicular body protein 8, increased sodium tolerance 1 homolog, overexpressed in lung cancer 1, putative MAPK-activating protein PM28
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP53990
- Protein NameIST1 homolog
- Scientific DescriptionProposed to be involved in specific functions of the ESCRT machinery. Is required for efficient abscission during cytokinesis, but not for HIV-1 budding. The involvment in the MVB pathway is not established. Involved in recruiting VPS4A and/or VPS4B to the midbody of dividing cells.
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161