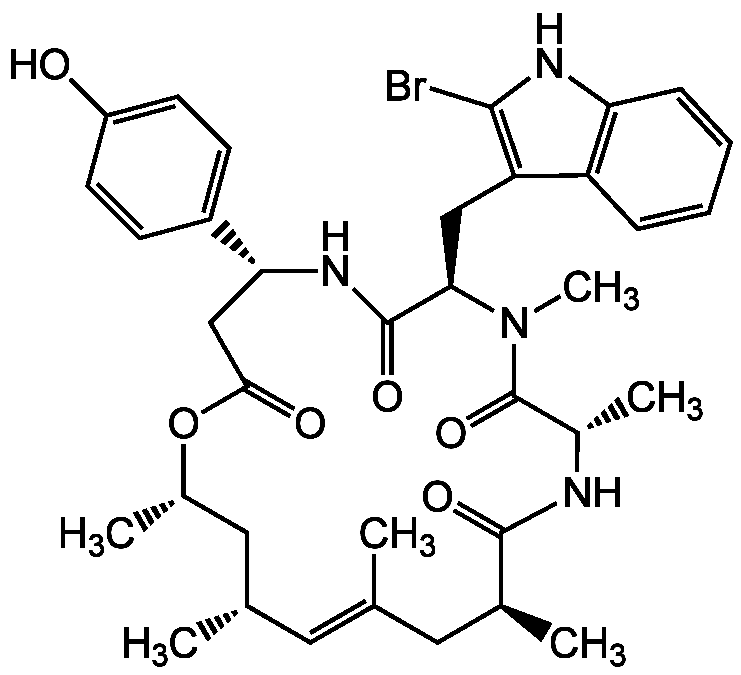
Chemical Structure
Jasplakinolide (high purity) [102396-24-7] [102396-24-7]
AG-CN2-0037
CAS Number102396-24-7
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight709.7
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameJasplakinolide (high purity) [102396-24-7] [102396-24-7]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number102396-24-7
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Hazard InformationWarning
- Molecular FormulaC36H45BrN4O6
- Molecular Weight709.7
- Scientific DescriptionCell permeable, non-fluorescent F-actin probe [3, 8, 12]. Potent inducer of actin polymerization and stabilization [3, 8, 12]. Competes with phallotoxins for actin binding [3]. Antifungal and antiparasitic compound [1, 2, 9]. Antiproliferative and anticancer compound [3, 4, 5]. Apoptosis enhancer/inducer [6, 10]. Tool used for autophagy/phagocytosis research [7, 11, 13]. - Chemical. CAS: 102396-24-7. Formula: C36H45BrN4O6. MW: 709.7. Isolated from Jaspis splendens. Cell permeable, non-fluorescent F-actin probe. Potent inducer of actin polymerization and stabilization. Competes with phallotoxins for actin binding. Antifungal and antiparasitic compound. Antiproliferative and anticancer compound. Apoptosis enhancer/inducer. Tool used for autophagy/phagocytosis research.
- SMILESC[C@H]1C[C@@H](C)\C=C(C)\C[C@H](C)C(=O)N[C@@H](C)C(=O)N(C)[C@H](CC2=C(Br)NC3=C2C=CC=C3)C(=O)N[C@H](CC(=O)O1)C1=CC=C(O)C=C1
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12352200

![Jasplakinolide [102396-24-7] [102396-24-7]](https://www.targetmol.com/group3/M00/02/DB/CgoaEWY7OnmEcvKKAAAAAMWsCYE562.png)