Chemical Structure
JC-1 [3520-43-2,47729-63-5] [3520-43-2]
AG-CR1-3568
CAS Number3520-43-2
Product group Chemicals
Estimated Purity>98%
Molecular Weight652.2
Overview
- SupplierAdipoGen Life Sciences
- Product NameJC-1 [3520-43-2,47729-63-5] [3520-43-2]
- Delivery Days Customer10
- CAS Number3520-43-2
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- Estimated Purity>98%
- Molecular FormulaC25H27Cl4IN4
- Molecular Weight652.2
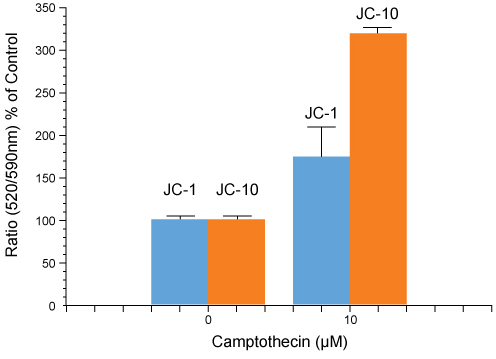
- Scientific DescriptionChemical. CAS: 3520-43-2 and 47729-63-5. Formula: C25H27Cl4IN4. MW: 652.2. The membrane-permeant dual-emission potential-sensitive JC-1 dye is widely used in apoptosis studies to monitor mitochondrial health by flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy and in microplate-based fluorescent assays. JC-1 dye can be used as an indicator of mitochondrial membrane potential in a variety of cell types, including myocytes and neurons, as well as in intact tissues and isolated mitochondria. JC-1 accumulates in mitochondria, selectively generating an orange J-aggregate emission profile (590 nm) in healthy cells. After cell injury, as membrane potential decreases, JC-1 monomers are generated, resulting in a shift to green emission (529 nm). The principal advantage of JC-1 relative to other commonly employed fluorescent probes of mitochondrial membrane potential is that it allows qualitative visualization, considering the shift from orange to green fluorescence emission, and quantitative detection, considering the fluorescence intensity ratio. - The membrane-permeant dual-emission potential-sensitive JC-1 dye is widely used in apoptosis studies to monitor mitochondrial health by flow cytometry, fluorescence microscopy and in microplate-based fluorescent assays. JC-1 dye can be used as an indicator of mitochondrial membrane potential in a variety of cell types, including myocytes and neurons, as well as in intact tissues and isolated mitochondria. JC-1 accumulates in mitochondria, selectively generating an orange J-aggregate emission profile (590 nm) in healthy cells. After cell injury, as membrane potential decreases, JC-1 monomers are generated, resulting in a shift to green emission (529 nm). The principal advantage of JC-1 relative to other commonly employed fluorescent probes of mitochondrial membrane potential is that it allows qualitative visualization, considering the shift from orange to green fluorescence emission, and quantitative detection, considering the fluorescence intensity ratio.
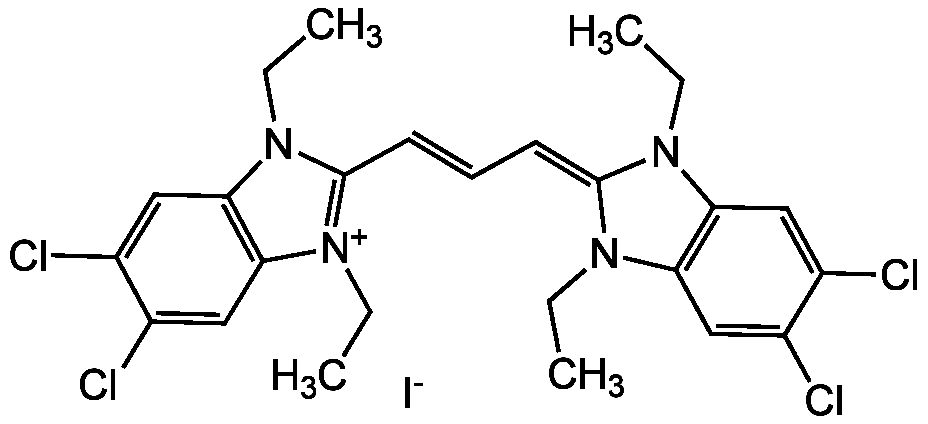
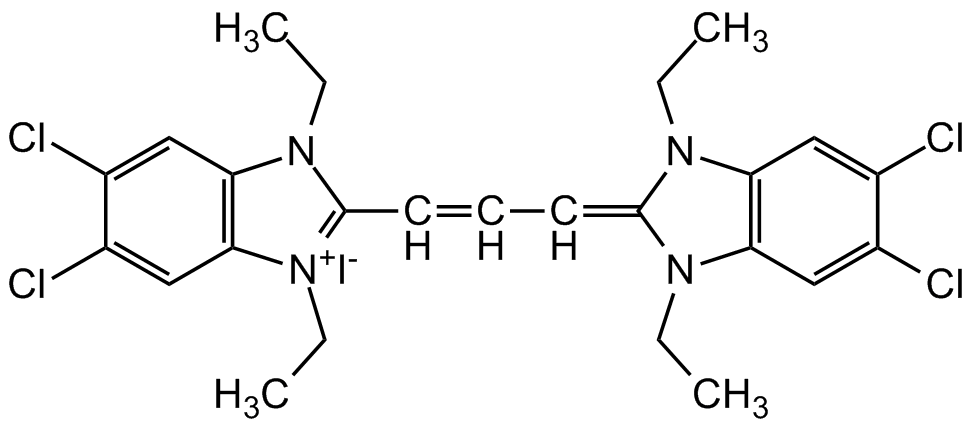
- SMILES[I-].CCN1C(=CC=CC2=[N+](CC)C3=C(C=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C3)N2CC)N(CC)C2=C1C=C(Cl)C(Cl)=C2
- Storage Instruction-20°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC12162000