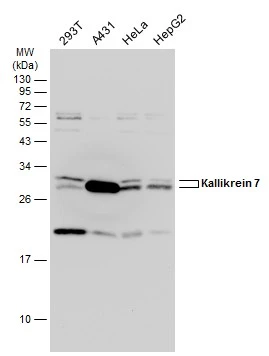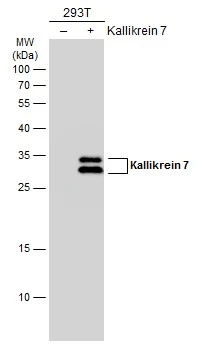
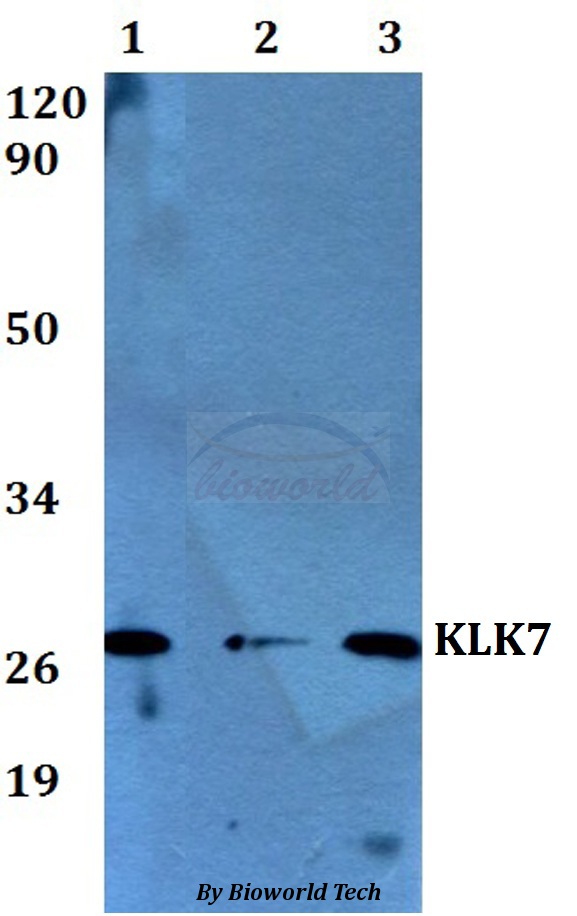
Non-transfected (–) and transfected (+) 293T whole cell extracts (30 μg) were separated by 12% SDS-PAGE, and the membrane was blotted with Kallikrein 7 antibody (GTX103548) diluted at 1:5000. The HRP-conjugated anti-rabbit IgG antibody (GTX213110-01) was used to detect the primary antibody.
Kallikrein 7 antibody
GTX103548
ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
Product group Antibodies
ReactivityHuman, Mouse
TargetKLK7
Overview
- SupplierGeneTex
- Product NameKallikrein 7 antibody
- Delivery Days Customer9
- Application Supplier NoteWB: 1:1000-1:10000. IHC-P: 1:100-1:1000. *Optimal dilutions/concentrations should be determined by the researcher.Not tested in other applications.
- ApplicationsWestern Blot, ImmunoHistoChemistry, ImmunoHistoChemistry Paraffin
- CertificationResearch Use Only
- ClonalityPolyclonal
- Concentration0.69 mg/ml
- ConjugateUnconjugated
- Gene ID5650
- Target nameKLK7
- Target descriptionkallikrein related peptidase 7
- Target synonymsPRSS6, SCCE, hK7, kallikrein-7, kallikrein 7 (chymotryptic, stratum corneum), serine protease 6, signal protein, stratum corneum chymotryptic enzyme
- HostRabbit
- IsotypeIgG
- Protein IDP49862
- Protein NameKallikrein-7
- Scientific DescriptionKallikreins are a subgroup of serine proteases having diverse physiological functions. Growing evidence suggests that many kallikreins are implicated in carcinogenesis and some have potential as novel cancer and other disease biomarkers. This gene is one of the fifteen kallikrein subfamily members located in a cluster on chromosome 19. Its encoded enzyme is thought to be involved in the proteolysis of intercellular cohesive structures preceding desquamation, which is the shedding of the outermost layer of the epidermis. Alternative splicing of this gene results in two transcript variants encoding the same protein. [provided by RefSeq]
- ReactivityHuman, Mouse
- Storage Instruction-20°C or -80°C,2°C to 8°C
- UNSPSC41116161

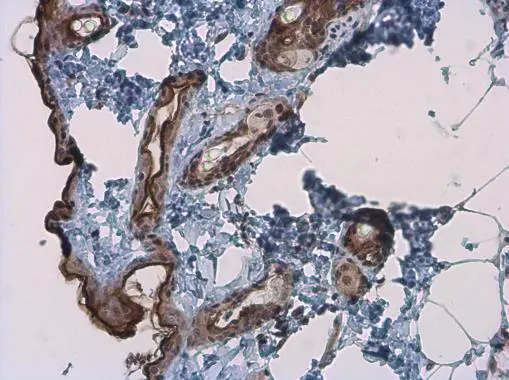
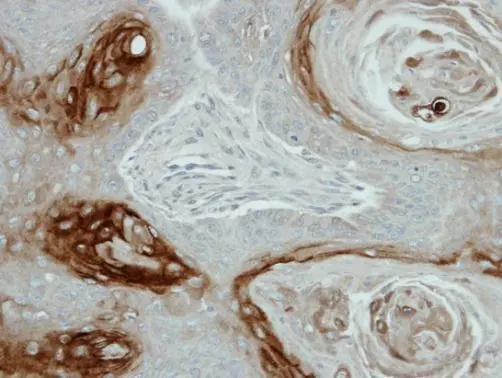


![IHC-P analysis of human squamous cell carcinoma (SCC) from skin tissue using GTX04475 Kallikrein 7 antibody [MSVA-707M] HistoMAX?. Squamous cell carcinoma showing strong kallikrein 7 staining in areas of keratinization.](https://www.genetex.com/upload/website/prouct_img/normal/GTX04475/GTX04475_20230728_IHC-P_70_23072722_439.webp)